Table of Contents
Some terms in trading sometimes sound the same. There are a lot of job roles in finance.
Financial engineering and quantitative finance are essential disciplines that play a crucial role in the modern economy. These fields involve applying advanced mathematical and statistical methods to the analysis and management of financial risk, allowing businesses and investors to make well-informed decisions about their finances.
By leveraging cutting-edge technology and tools, financial engineers can design sophisticated financial instruments that help businesses manage risk exposure and maximize return on investment. Furthermore, quantitative finance allows us to better understand complex financial markets by analyzing large datasets, which can inform investment strategies and mitigate potential risks. Overall, these fields provide a robust set of tools for understanding and managing the complex world of finance, making them essential for anyone involved in this rapidly-evolving sector.
What is the difference between financial engineering and quantitative finance?
The Difference between quantitative finance and financial engineering is that experts in quantitative finance or Quants deal with one particular niche in finance (usually implements complex models). In contrast, financial Engineers are practitioners with broad expertise who use mathematical techniques to solve problems.
Financial analysts (specific tasks) evaluate projects, businesses, and budgets, the difference between financial analysis and financial engineering. Financial engineers (broad tasks) are practitioners with broad expertise working with insurance companies, asset management firms, hedge funds, and banks.
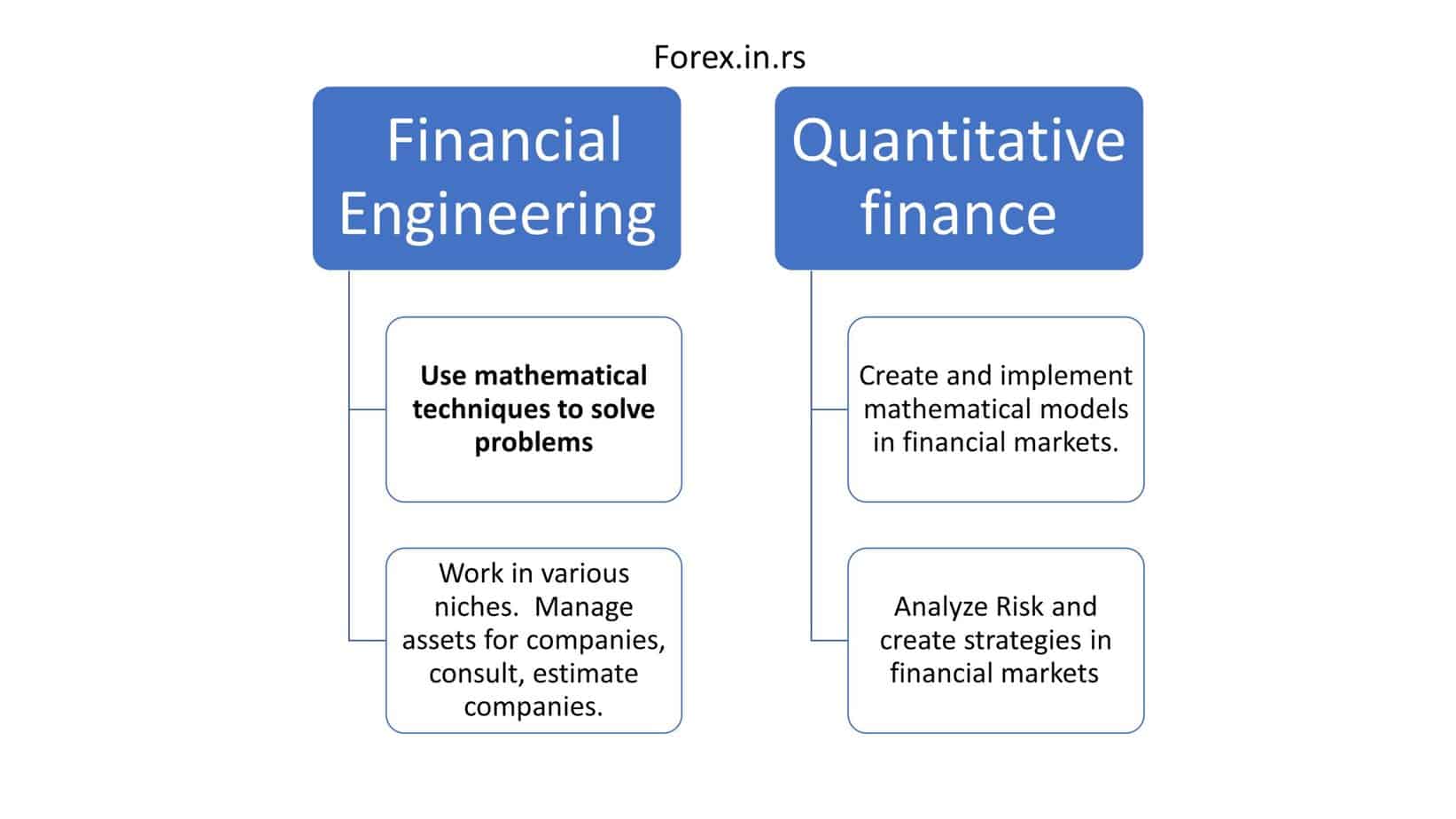
Financial engineering vs. quantitative finance
- Financial Engineers are practitioners with broad expertise, while quantitative finance work in the financial models and strategies niche.
- Quantitative finance develops complex models and implements trading strategies, while Financial Engineers create models for corporations to help them manage their assets and liabilities.
But let us analyze deeper these job roles more.
Financial Engineering
The term financial engineering is related to the application of mathematical techniques to solve financial problems. Financial Engineering is a profession where engineers create products to help a given company, and quantitative finance is a profession where experts use math and statistics to measure risk or invest money for a fund.
The difference between these two names gives us some idea about what we should be looking for, but there is a lot more to think about whenever we look at these words.
Developing applications with Mathematical theory related to Measure theory, Applied Walks, Continuous Stochastic Processes, Ito Calculus, Stochastic Differential Equations, and Martingales, more akin to the Sciences, such as Physics, Mathematics (a more rigorous level of Mathematics) are all seen as Mathematical Finance.
Is financial engineering complex?
No, financial engineering isn’t challenging more than any other engineering position. The most critical impact of the job’s degree of difficulty is related to company organization and workers’ overload. Companies seek engineers in math, statistics, stochastic calculus, and programming at various skill levels.
Main facts about Financial engineering
- Financial engineering involves option pricing, Secularization, and Products of Structured Finance. It is not as rigorous as Mathematical Finance and is more focused on a specific problem of financing the complex structure.
- Financial engineering involves the practice of programming, economic theory, tools of mathematics, and methods of engineering:
- People have seen technical methods, more computational finance, and mathematical finance in the financing practice.
- Even though several financial engineers have studied engineering before and some Universities offer postgraduate degrees in this field, they have requested that applicants have an engineering background, even though financial engineering does not fit in with traditional professional engineering.
- The Accreditation Board for Engineering and Technology (ABET) offers no accreditation for financial engineering degrees in America.
- The International Association of Quantitative Finance provides certification for the financial accreditation program.
- Tools from applied mathematics, statistics, and economic theory, computer science are used in Financial engineering.
- Persons who use technical, financial tools, such as computer programmers in banks or statisticians who work in the government economic bureau, are seen as financial engineers.
- Even though many practitioners restrict the term to educated persons in the full range of modern finance tools, their work has to be informed by financial theory.
- Persons have even applied more restrictions and only consider those who originate new financial strategies and products.
- Financial engineering is significant for persons who are involved in customer-driven derivative businesses.
- Finance engineering includes programming and quantitative modeling, risk managing derivative products, and trading to comply with regulations and Basel Capital/liquidity requirements.
A career as a financial engineer involves using advanced mathematical and computational techniques to help large corporations manage their assets and liabilities. This may include consulting with clients to determine the nature of their financial challenges, developing solutions based on industry trends and market conditions, researching new financial products, and developing models to improve existing products.
To be successful in this role, a financial engineer must have excellent knowledge of financial concepts and principles, as well as a deep understanding of the inner workings of large corporations. They must also have strong analytical skills and the ability to communicate effectively with clients and management about the results of their analysis.
Some essential duties of a financial engineer may include conducting audits and analyzing performance data, estimating interest rates and inflation rates that affect cash flow, developing investment strategies for individuals or companies, working with management to create budgets and monitor performance over time, and developing models to assess risk.
If you are interested in pursuing a career in financial engineering, you will need strong quantitative skills and an aptitude for complex mathematics. It would help if you also were comfortable working with computers, software programs, and other technology-related tools. You can become a successful financial engineer with dedication and hard work and help large corporations achieve their goals.
What is a Quantitative analyst?
Quantitative analyst or Quant covers all persons who work with math for practical purposes, such as financial engineers. In addition, quants usually specialize in specific areas such as risk management, derivative structuring or pricing, algorithmic trading, and investment management.
A quantitative analyst is a professional who uses mathematical or statistical techniques to solve practical financial issues. This may include managing risk, trading securities, pricing derivatives, or regulating financial markets.
To be successful in this role, a quantitative analyst must have strong knowledge of the financial industry and the current market conditions. They must be able to identify and analyze trading strategies, evaluate system performance, and develop new analytical software for their work.
In addition to these technical skills, a quantitative analyst must also be able to collaborate effectively with other analysts and product development teams. They must communicate clearly about their work and establish efficient data collection methods that can be updated.
If you are interested in pursuing a career as a quantitative analyst, you must have strong analytical skills, advanced math or statistics knowledge, and excellent communication abilities. With these skills, you can help your company stay ahead of the competition by providing valuable insights into market trends and performance metrics.
The first-generation Financial quants to arrive on Wall Street in the late 1970s to early 1980s adopted the names Rocket Scientists or aerospace engineers; an older term used when rockets were developed by Werner Van Braun or WWII and, more recently, the NASA space program.
Disruptive innovation, which includes fondness and adventurousness, is synonymous with financial engineering.
Financial ’Rocket scientists“ trained in statistics or finance and applied mathematics; they spent their whole careers doing risk-taking. They used mathematical techniques for financial jobs or worked for themselves because they were not hired for their mathematical abilities.
However, more recently, the financial engineers of this generation have been equipped with their PhDs in physics and mathematics, and they started their careers in non-financial fields of academics.
What is Quantitative finance?
Quantitative finance or Mathematical finance is applied mathematics in one place if you are only interested in the mathematical modeling of financial markets. Mathematical finance will widen the numerical or mathematical models without connecting with economic theory.
Mathematical consistency is needed, not like economic theory. Therefore a financial economist may study the structural reasons behind the share price of a particular company. In contrast, a financial mathematician would settle for the price they are given without checking anything, or they would use stochastic calculus to find the equal value of derivatives of the stock (see: Financial modeling; Asset Pricing; Valuation of options). In mathematical finance, the fundamental theorem of arbitrage-free pricing is crucial. However, the Black-Scholes formula and equation are found in the key results.
In the early 1990s, first-degree programs were set up for Financial Engineering, but the number of programs has increased rapidly. As a result, people now refer to those with a degree in the field as ’financial engineers“.
The fields of computational finance and financial engineering have been overlapped heavily by Mathematical finance. Financial engineering focuses on modeling and application; stochastic asset models often assist here. Simultaneously, Mathematical finance focuses on building tools of implementation for the models generally and analysis. Advanced quantitative techniques are required for both finance branches: derivatives pricing on one side and risk- and portfolio management on the other.
Interesting fact:
Louis Bachelier, a French mathematician, is the author of the first scholarly work on mathematical finance; mathematical finance became a discipline in the 1970s even though the work was published in 1900. It followed the work of Robert Merton, Fischer Black, and Myron Robert on option pricing theory.
Many degrees and research programs are being offered today for Mathematical financing.
























