Regarding market capitalization, no other exchange is more significant than the Forex market, generating more than $5 trillion worth of daily trades. It is no wonder that the latter is the premier destination for people with high financial aspirations.
Some refer to futures and forex interchangeably, although the two financial instruments vary considerably. Both are traded similarly and subject to the same technical analytics. One such analytics tool is “standard deviation,” but what exactly is it?
This post will review the meaning of standard deviation as applicable in forex and how to use it to improve your trading strategy.
What is the Deviation in Forex?
In trading, deviation in forex represents slippage. During high volatility, slippage or deviation in forex occurs when a trade order is filled at a price different from the requested price.
Forex deviation has two meanings in trading literature. The first meaning equates the term forex deviation with the term standard deviation. Standard deviation is a statistical term that refers to price volatility in any currency and measures how widely price values are dispersed from the mean or average.
Learn more about low-slippage brokers.
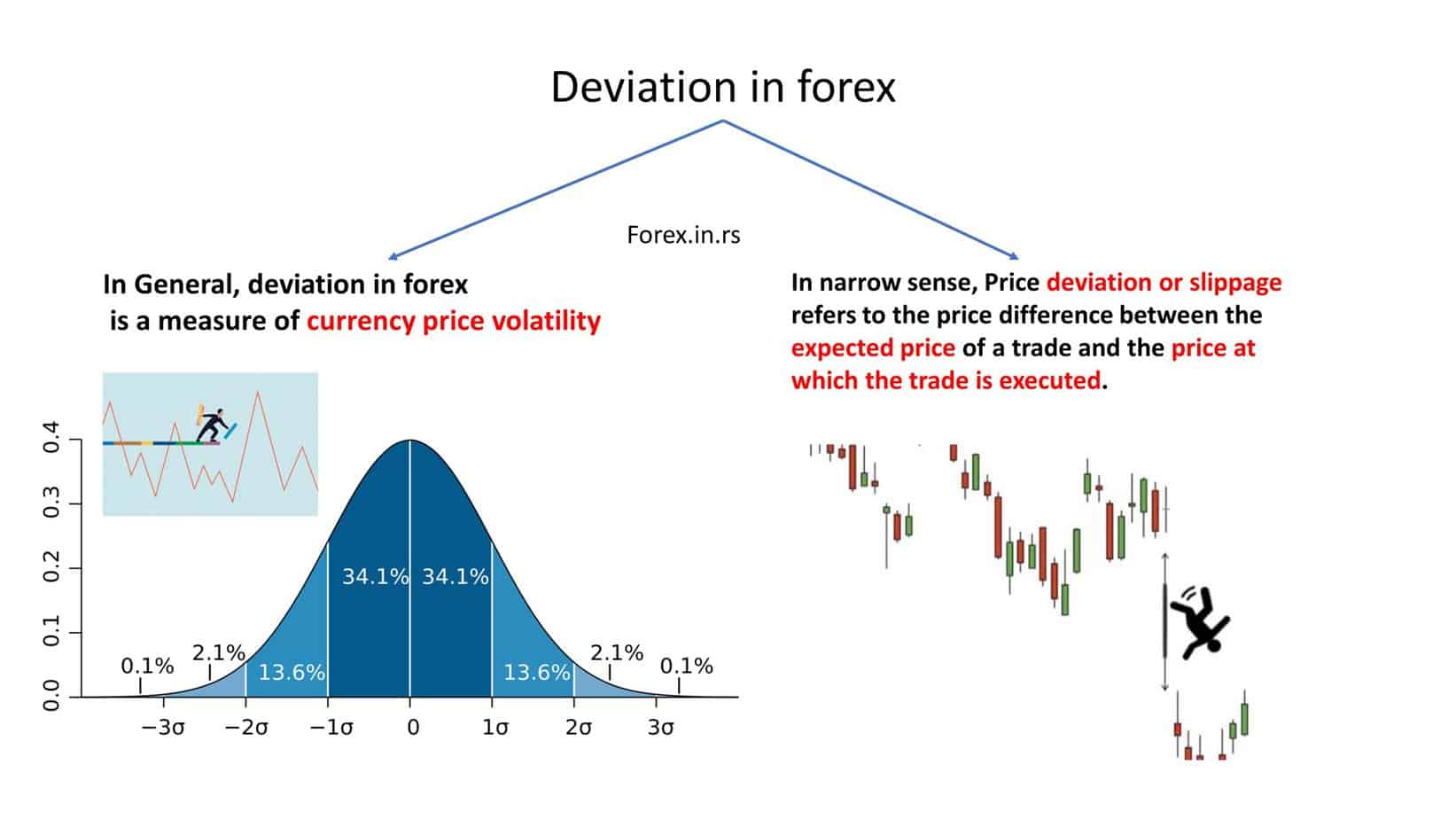
The second meaning equates the term forex deviation with the term slippage. Slippage is the difference between the expected price of a trade and the price at which the trade is executed and usually occurs during periods of higher volatility.
- Definition:
- Slippage occurs when the execution price of an order is different from the expected price.
- Causes:
- Market Volatility: Sudden price jumps or falls due to economic news or events.
- Low Liquidity: Fewer market participants can lead to gaps in pricing.
- High Volume Orders: Larger orders might not be filled simultaneously, leading to multiple prices for a single trade.
- Market Gaps: When the market opens at a different price from its previous close, often seen over weekends or holidays.
- Latency: Delays in communication between the trader’s platform and the broker.
- Effects:
- Unpredictable Outcomes: Trades might result in more or less profit or loss than expected.
- Increased Risk: Slippage can exacerbate losses, especially in volatile markets.
- Limiting Slippage:
- Limit Orders: Only execute if the price is at or better than a specified level.
- Stop-Limit Orders: Combines features of stop and limit orders to ensure a specific price range.
- Trade Timing: Avoid trading during major economic announcements or market openings/closings.
- Use Reputable Brokers: Ensure fast execution speeds and stable platforms.
- Types of Slippage:
- Positive Slippage: The order is executed at a better price than expected. (e.g., a buy order executed at a lower price than anticipated).
- Negative Slippage: The order is executed at a worse price than expected. (e.g., a buy order executed at a higher price than anticipated).
- Not Always Negative:
- While traders often view slippage in a negative light due to unforeseen losses, it’s possible to experience positive slippage, which results in better-than-expected trade outcomes.
Remember, while slippage is inherent in trading, particularly in the fast-paced forex market, understanding its causes and effects can help traders devise strategies to manage or minimize its impact.
If you’ve been in the forex market for some time, you probably know all too well how dangerous spikes in volatility can be. Such spikes can easily result in severe losses in one’s trading positions. This is where a good understanding of standard deviation can prove helpful. How is this so?
Standard deviations are used to determine the inherent volatility of a currency pair before placing a trading order. The latter is a standard statistical technique that measures a dataset’s variance from its’ original value. The more a value drops in proportion to its initial value, the bigger the standard deviation.
Today, the standard deviation applies to many discipline areas, such as academics, healthcare, and forex trading! In the case of the latter, standard deviations are primarily used to measure volatility. Many traders use it to visualize the relationship between a currency’s closing price and its average or mean value over a specific period.
To use standard deviation in forex, traders need to establish three things:
Determine the closing price over a certain period. Establish the mean value for the dataset. Calculate the difference between the closing price and the mean value
Of course, calculations for standard deviation are much more complicated than expected. For this reason, traders often depend on popular trading platforms with a deviation tool that handles the calculations for them.
You must always set deviation for quoted prices well in the MT4 platform because of the possible error “off quotes” MT4.
How do we set deviation in the forex MT4 platform?
In MetaTrader 4 (MT4), “deviation” refers to the allowable slippage value when entering a trade. By setting a deviation, traders can control the price slippage they will accept on an order.
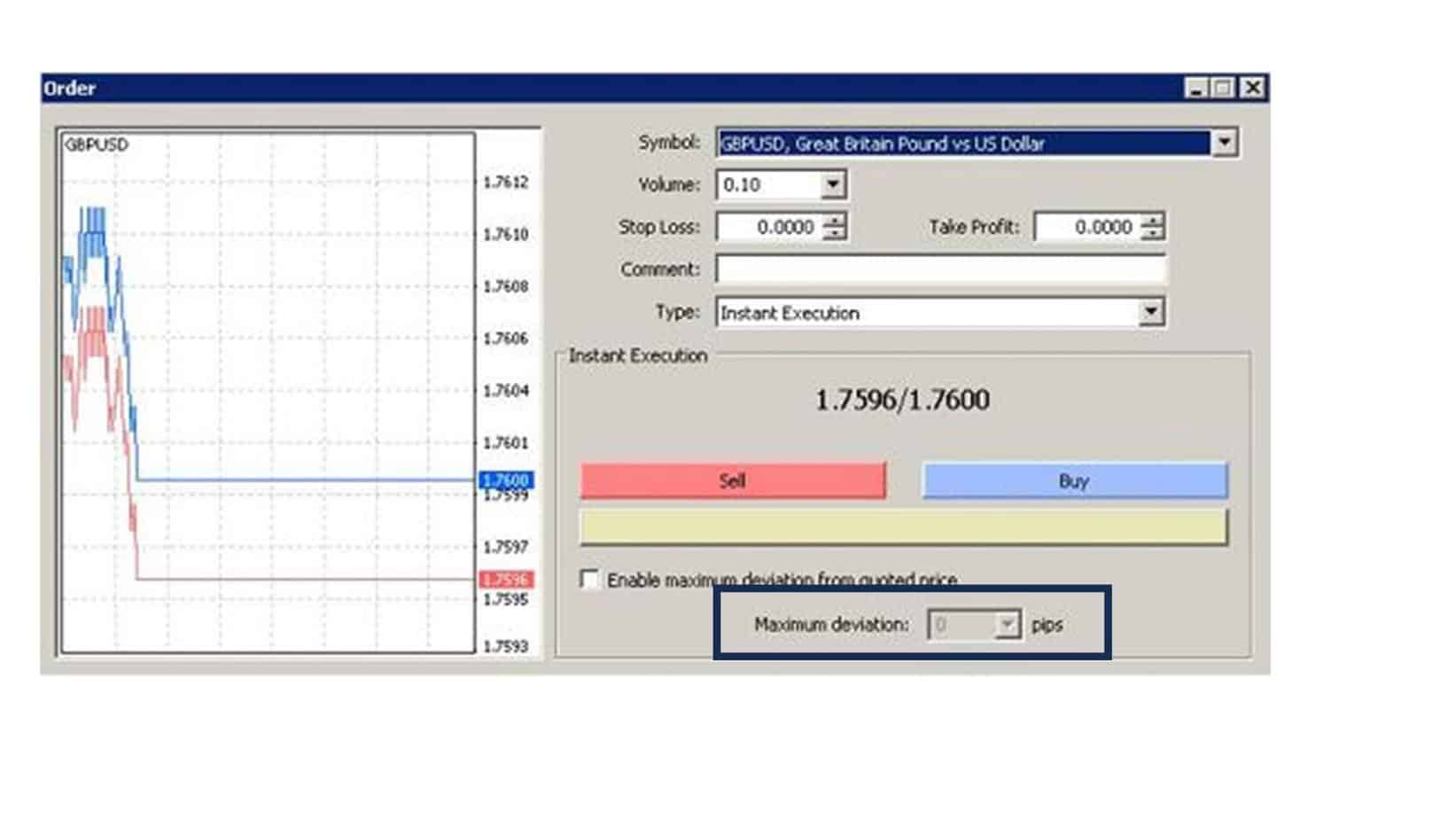
Here’s how to set the deviation in MT4:
- Open MT4 Platform: Launch your MetaTrader 4 trading platform.
- New Order Window:
- Click on the “New Order” button in the top toolbar.
- Alternatively, you can right-click on the currency pair in the “Market Watch” window and select “New Order.”
- Selecting the Deviation:
- In the “New Order” window, you’ll see an option for “Type.” If you choose “Instant Execution,” you can set the deviation.
- Right beside the “Type,” there’s a field named “Deviation.” Here, you can set the acceptable slippage for your order in pips.
- Input Value:
- Enter the number of pips you’re willing to accept as slippage. For example, if you enter “2” in the deviation box, you’re allowing the trade to be executed at a price two pips worse than the currently displayed price.
- Completing the Order:
- Once you’ve set your desired deviation, you can proceed to fill out the other order details (e.g., volume, stop loss, take profit) and then click on “Sell” or “Buy” to execute the trade.
- Check Deviation Settings:
- Some brokers might have a default deviation set up. It’s always a good idea to double-check this value before placing a trade, especially in volatile market conditions, to ensure you’re comfortable with the potential slippage.
- Modifying Default Deviation:
- If you want to change the default deviation setting, go to “Tools” in the menu bar, then “Options,” and then the “Trade” tab. Here, you can set a default value for deviation.
Setting a deviation doesn’t guarantee your order will be executed, especially in highly volatile markets. If the price moves beyond your set deviation before the order is executed, the order might be rejected, and you might receive a requote depending on your broker’s settings.
Conclusion
Deviation, commonly called slippage in forex, represents the difference between a trader’s expected order price and execution price. This phenomenon primarily arises due to market volatility, sudden economic news, or low liquidity conditions.
While slippage can work in favor of and against a trader, it introduces an element of unpredictability in trade outcomes. Therefore, understanding and managing deviation is essential for traders to mitigate potential risks. By using tools like setting appropriate deviation values in trading platforms, traders can exert some control over the extent of slippage they’re willing to accept.
























