Table of Contents
Risk in trading refers to the potential for financial loss or underperformance relative to expectations when engaging in financial market transactions. This risk stems from market volatility, where asset prices fluctuate unpredictably due to economic changes, political events, or investor sentiment. Additionally, risks can arise from inadequate knowledge or experience, leading to poor decision-making in complex and often fast-paced trading environments. Furthermore, leverage, or using borrowed funds, can amplify gains and losses, adding another layer of risk to trading activities.
What is the risk in forex trading?
Risk in trading implies future uncertainty about deviation from expected earnings or expected outcomes. Usually, the most significant risk for traders is uncontrolled loss of capital. High risk in trading causes around 95% of forex traders to lose money.
Leverage in trading is borrowed capital to increase the potential returns, and in the forex market, high leverage is up to 1:1000. So traders can trade with more money than they have.
Risk percentage = Risk / Capital
But there is a problem: high risk in trading causes 95% of traders to lose money. Traders need to know risk management trading forex rules.
Look at this table again and again:
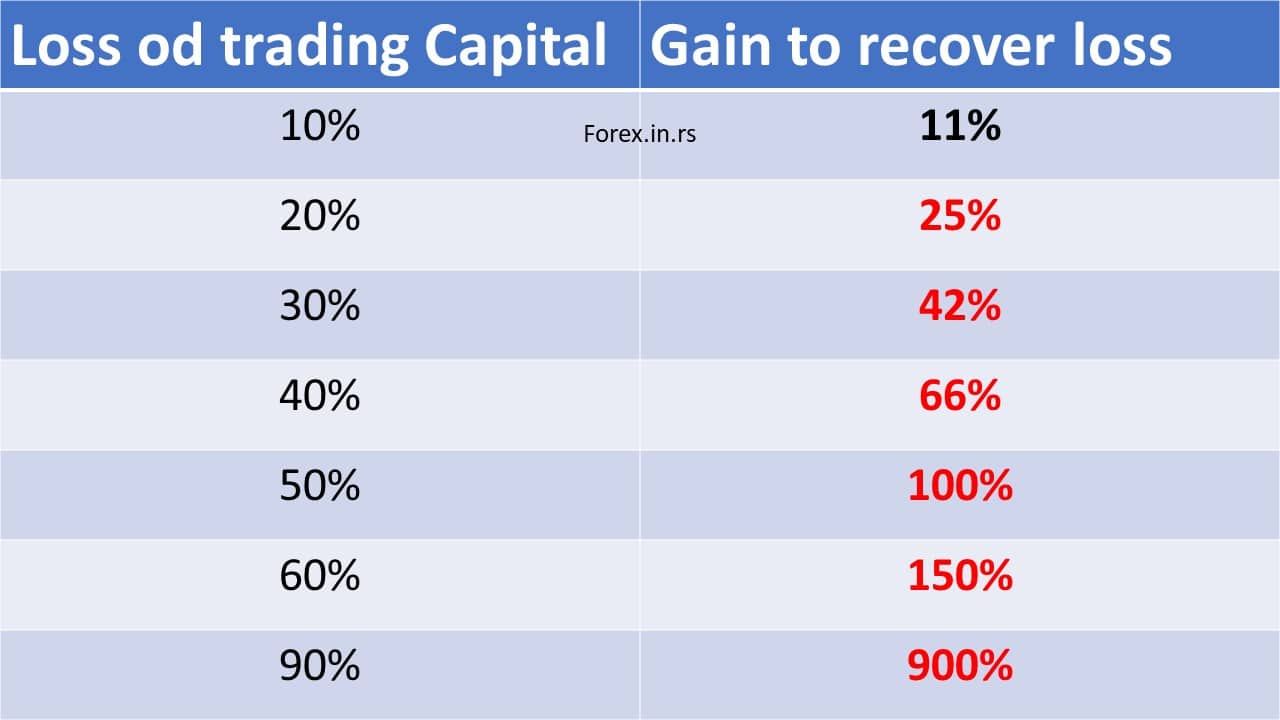
As we know, if a trader takes a risk and makes a drawdown, they will need more money to recover. If you lose 50% of your equity, you must earn 100% to recover.
The “90-90” rule in Forex trading is an informal observation suggesting that 90% of retail traders lose 90% of their invested funds within the first 90 days of trading. Although not a precise statistic, this rule highlights the high risk and rapid losses many inexperienced retail traders face, primarily due to their engagement in high-risk trading strategies. It is a cautionary note about the challenges and potential pitfalls in the volatile Forex market, particularly for those new to trading.
The main reason why many traders don’t make money is not because of inexperience but from the poor risk management trading Forex. Due to the unpredictable nature of the Forex market, it is hazardous. Hence, Forex risk management is considered the success factor irrespective of whether you are a professional or a new trader.
In this article, you will get an insight into the top risk management strategies that will help you make profits and avoid a loss to have a good experience while trading Forex.
Practical risk management strategies in forex trading
In prop companies, traders will get Risk management rules, and for example, it looks like this:
1) Do not fall below X% relative drawdown—for example, 2% or 4%.
2) Do not fall below X% absolute drawdown. For example, absolute drawdown is the sum difference between the initial capital risk and a minimal point below that level, and many companies are set to be 5%.
3) Do not risk over X% on each Trade—for example, 1% per Trade or 0.5% per Trade, etc.
4) Do not have more than 2% weekly drawdown. In that case, if some trader has above 2%, they will not trade that week anymore.
5) Position size needs to be calculated based on this formula.
Of course, rules can be more detailed; this is just an example.
Risk management strategies are related to position size calculation, too.
Position size = Winrate – ( 1- Winrate / Risk Reward Ratio) is an example of the Kelly criterion (one of the simplest), but traders use their formulas in many companies.
If you trade alone, you must define your rules and stick to those rules as a retail trader. If you lose more than you wished on this day or week – stop trading and wait for next week. Do not chase for profit.
Risk management strategies in forex trading are:
- Have a proper understanding of the risks involved in trading Forex
- Make use of stop-loss in managing Forex risks.
- Never risk further if you can’t lose more.
- Limit the use of leverage in managing Forex risk
- Never have unrealistic profit expectations while managing risks.
- Manage Forex trading with take-profit
- Have a proper plan in Forex trading
- Always prepare for the worst.
- Expand your Forex portfolio
- Try to control your emotions.
If you are new to trading, the best thing you can do is educate yourself. Remember that your approach towards Forex trading should be similar to any career you need to learn about the subject in detail.
However, a diverse range of resources, such as Forex videos, webinars, and articles, can provide you with the absolute knowledge you seek. After gathering sufficient information on the various aspects of Forex trading, you can test yourself by opening a demo account.
The foreign exchange market and risk management are based on the trader’s plan for when and how many lots they will trade.
The maximum recommended exposure in most online articles for retail traders is 2%, where traders risk no more than 2% of their available capital. My prop company’s maximum risk is 0.5% per position and a maximum weekly drawdown of 2%. This is forex exposure management.
By using virtual funds, you can use the free account to trade Forex. Such an account will help you trade in the markets without any risks. As such, you will know the functioning of Forex markets, the different trading platforms, and various trading strategies.
Use of Stop-Loss in Forex Trading
In the dynamic and often unpredictable world of Forex trading, employing a stop-loss strategy is a fundamental practice for managing risk. A stop-loss is an automatic safety switch for trading positions set at a predetermined price point. The Trade is closed when the market hits this price, capping potential losses. This tool is indispensable in safeguarding a trader’s capital against sudden market movements.
- Essential Risk Management Tool: Stop-loss orders are a fundamental component of risk management in trading, acting as an automatic mechanism to limit potential losses.
- Automatic Trade Closure: A stop-loss automatically closes a trade at a pre-set price, preventing more significant losses in volatile market conditions.
- Personal Trading Risk Tolerance: For individual traders, risking 1% of the trading balance per Trade is generally considered a safe threshold, balancing the potential for profit with the risk of loss.
- Proprietary Trading Firm Requirements: When trading for a proprietary (prop) firm, the risk per Trade often needs to be lower, typically around 0.25% to 0.5%. This is due to the firm’s risk management policies and the collective nature of the capital being traded.
- Adherence to Firm’s Drawdown Limits: Prop firms usually have strict drawdown limits, often around a maximum of 4%. A drawdown refers to the decline from a peak to a trough in the value of an investment or trading account.
- Customized Stop-Loss Strategies: Traders should tailor their stop-loss strategy based on whether they are trading personally or for a prop firm, respecting the different risk tolerances and rules.
- Regular Review and Adjustment: It’s essential to review and adjust stop-loss strategies based on market conditions and trading performance, ensuring they align with current risk management objectives.
- Protection Against Market Volatility: Stop-loss orders provide a safety net against sudden and unpredictable market movements, which is especially important in highly volatile markets like Forex.
- Disciplined Trading Practice: Consistently applying stop-loss orders instills discipline in trading practices, helping to avoid emotional decision-making and impulsive reactions to market changes.
Setting a stop-loss involves determining the optimal point at which a trade should be exited to minimize losses while allowing enough room for the usual market fluctuations. A well-adopted guideline is to set the stop-loss at a level where no more than 2% of the trading balance is risked on a single trade. This method ensures that losses are kept within a manageable range and helps preserve the trading capital over the long term.
Discipline plays a crucial role in the effectiveness of stop-loss orders. Once a trader sets these limits, it is vital to adhere to them. Altering or ignoring pre-set stop-loss orders can lead to increased losses, negating the purpose of this risk management tool. It’s important to remember that a stop-loss is part of a strategic plan, not a reactive measure to be adjusted immediately.
Forex traders can access various stop-loss strategies tailored to different trading styles and experience levels. These include fixed stop-losses, where the price is set at a certain point; trailing stop-losses, which move with the market price; and more sophisticated, conditional stop-losses, which consider other market factors. Selecting the correct type of stop-loss strategy is critical and should be based on the trader’s individual risk tolerance, trading strategy, and experience.
Never risk further if you can’t lose more.
“Never risk further if you can’t lose more” is a fundamental principle in Forex trading risk management, emphasizing the importance of only risking what one can afford to lose. This rule is crucial, particularly for novice traders, who often fall into the trap of overextending themselves financially in the volatile Forex market.
The Peril of Over-Risking
- Inexperienced Trader Pitfall: New traders in the Forex market frequently make the mistake of risking more capital than they can afford to lose. This is partly due to a lack of understanding of market volatility and the risks involved.
- High Exposure to Market Risks: By investing more money than they can comfortably lose, traders expose themselves to significant financial risks. The Forex market is unpredictable, and positions can quickly move against a trader.
The Challenge of Recovering Lost Capital
- Difficulty in Recouping Losses: Once capital is lost in Forex trading, recovering it becomes a formidable challenge. The trader must generate significantly higher returns to recover the lost amount and cover additional costs, such as transaction fees.
- Increased Pressure Leading to Poor Decisions: Traders often attempt to recoup their losses by taking higher risks in subsequent trades. This approach is dangerous, particularly when the account balance is depleted, leading to increased risk and potential for further losses.
Adhering to the 2% Rule
- Risk Management Strategy: A well-established guideline in Forex trading is never to risk more than 2% of the account balance on a single trade. This rule helps maintain a balanced approach to risk, ensuring that traders do not expose themselves to excessive losses that can’t be quickly recovered.
- Importance of Position Sizing: As the account balance changes, so should the position size. If a trader’s capital decreases, they should proportionally reduce their trading size to maintain the risk level in line with their reduced capital.
Example Illustrating the Principle
- Initial Scenario: Consider a trader who starts with $100,000, trading one lot per Trade.
- After Losses: After 500 trades, if their balance drops to $50,000, continuing to trade with one lot is a strategic mistake. This is because the risk per Trade relative to their total capital has effectively doubled.
- Appropriate Adjustment: The trader should adjust the trading size to 0.5 lots to align with the decreased account balance. This adjustment helps maintain the risk per Trade at a consistent and manageable percentage of the account balance.
Leverage and Risk Management
Leverage in Forex trading is a critical factor in risk management, as it directly influences the degree of risk and potential return on a trade. Understanding its impact is crucial for effective risk management:
- Amplification of Gains and Losses: Leverage allows traders to control prominent positions with relatively little capital. This means that potential profits and losses are magnified in proportion to the leverage used. For example, with a high leverage, a slight price movement can lead to significant profits or losses.
- Increased Market Exposure: High leverage exposes traders to greater market risk. A highly leveraged position can quickly lead to substantial losses, potentially exceeding the initial investment, if the market moves unfavorably.
- Margin Calls and Liquidation Risks: Using leverage involves borrowing funds from the broker. If a leveraged position starts to incur losses, the broker may issue a margin call, requiring the trader to deposit additional funds. Failure to meet a margin call can result in the liquidation of the position, leading to significant losses.
- Risk of Overtrading: Leverage can tempt traders to open more prominent or more numerous positions than they would without it, leading to overtrading. Overtrading increases the risk of significant losses, especially if market conditions are volatile or unpredictable.
- Importance of Conservative Leverage for Beginners: For novice traders, high leverage can be hazardous due to their limited experience managing rapid changes and potential losses. It’s often advised that beginners use lower leverage to limit their risk exposure.
- Correlation with Stop-Loss Orders: Effective use of leverage is often paired with strict stop-loss orders. These orders help manage the risk by automatically closing a position at a predetermined loss threshold, which is crucial in leveraged trades due to the speed at which losses can accrue.
- Balancing Leverage and Risk Tolerance: The choice of leverage level should align with the trader’s risk tolerance and trading strategy. A more conservative trader might opt for lower leverage to manage risk more effectively, while a trader comfortable with high risk might choose higher leverage.
Never have unrealistic profit expectations while managing risks
Having realistic profit expectations is fundamental to managing risks effectively in Forex trading. Unrealistic expectations can lead to aggressive trading behaviors, often increasing risks and potential financial losses.
- Overestimation of Profit Potential: New traders often enter the Forex market with high expectations of quick and substantial profits. This overestimation can lead them to take precarious positions or employ aggressive trading strategies, believing higher risk equals higher returns.
- Aggressive Trading and Increased Risks: Driven by unrealistic profit goals, traders may engage in overtrading, use excessive leverage, or ignore risk management principles. Such behaviors significantly increase the likelihood of substantial losses, especially in the highly volatile Forex market.
- Importance of a Conventional Approach: Adopting a conventional, disciplined approach to trading with realistic goals is crucial, especially for beginners. This involves understanding market dynamics, using proven trading strategies, and setting achievable profit targets.
- Learning from Mistakes: Realistic expectations allow traders to analyze their trading decisions and outcomes objectively. Recognizing and accepting when a trade is unfavorable enables a trader to exit the position and limit losses rather than hoping unrealistically for a turnaround.
- Avoiding Greed-Driven Decisions: Unrealistic profit expectations often lead to decisions fueled by greed rather than sound trading strategies. Greed can cloud judgment, leading to poor trading choices and increased susceptibility to market pitfalls.
- Managing Emotional Responses: Realistic expectations help manage emotional responses to market movements. Traders are less likely to experience extreme stress or make impulsive decisions driven by fear or excitement, often leading to trading mistakes.
- Sustainable Trading Strategy: Setting realistic profit expectations is integral to developing a sustainable long-term trading strategy. It encourages consistent and steady trading practices, which are more likely to yield positive results.
Trading Plan Before Trading is Important
A proper plan is an essential component of risk management in Forex trading. A well-structured trading plan helps navigate the market’s complexities and mitigate potential risks.
Trader Profile:
- Name: Emily
- Trading Capital: $10,000
- Risk Tolerance: Conservative
- Experience Level: Intermediate
Trading Plan:
- Risk Management Strategy:
- Maximum Risk Per Trade: 1% of capital ($100 per Trade).
- Stop-Loss and Take-Profit: Set stop-loss at 1% below the entry point and take-profit at 2% above the entry point to maintain a 1:2 risk-reward ratio.
- Leverage: Use a maximum leverage of 1:10 to control exposure.
- Trade Selection Criteria:
- Market Analysis: Use a combination of technical analysis (like moving averages and RSI) and fundamental analysis (like economic news and interest rates).
- Currency Pairs: Focus on significant pairs (e.g., EUR/USD, USD/JPY) for lower spreads and better liquidity.
- Trade Execution:
- Entry Points: As technical indicators indicate, enter trades at the beginning of a trend,
- Trade Duration: Aim for medium-term trades (holding positions for several days to a week).
- Monitoring and Adjustment:
- Regular Review: Check open positions at least twice a day.
- Adjustments: If the market moves against a position, but the overall trend seems intact, adjust the stop-loss to minimize potential loss.
- Emotional Control:
- Avoid impulsive decisions; stick to the pre-defined plan.
- Take breaks from trading after a loss to avoid emotional trading.
Example Scenario:
Emily decides to trade the EUR/USD pair. She observes that the pair is starting an uptrend based on her technical analysis. She enters a long position at 1.1200.
- Trade Size: $10,000 (her entire capital, utilizing 1:10 leverage).
- Risk Per Trade: $100 (1% of her $10,000 capital).
- Stop-Loss: Set at 1.1080 (1% below her entry point).
- Take-Profit: Set at 1.1420 (2% above her entry point).
After a day, the EUR/USD pair initially dips to 1.1150 but then rises. Emily’s analysis still supports an uptrend, so she holds her position. By the end of the week, the pair hits her take-profit level at 1.1420, and her Trade is closed automatically for a profit.
Always prepare for the worst
As mentioned, the Forex market is very unpredictable. Despite this, much evidence in past events shows how a market reacts in a particular situation. Previous happenings or events might not be repeated but show a trend.
Hence, it is crucial to consider the history of a particular currency pair that you are trading. Develop an action plan that will save you from a bad situation if that happens. It is unwise to underestimate the possibilities of sudden price movements. As such, you need a plan that will sail you through it.
Try to control your emotions.
When trading in Forex, you should know how to control your emotions. Failing to monitor your emotions won’t allow you to reach a suitable position to earn trading profits. That’s because emotional traders find it hard to adhere to trading strategies and rules.
Stubborn traders will not exit despite losing streaks and expect to come out with shining colors after a few trades. But such a thing might never happen. A wise trader will withdraw after realizing the mistake with the most minor loss.
Once out, they will be patient and enter the market whenever an opportunity appears. A trader on a winning streak might become greedy and stop following the proper risk management strategies.
Conclusion
The best way for Forex trading work will vary from one trader to another and depend on their perspectives. Some traders will take more calculated risks than others. It is recommended to start practicing in a conventional way of reducing risk. Do not chase for profit; wait for the opportunity, and think about risk every day.
























