In finance, it is implied that the value of the money will increase over time if invested properly. The value of money received at present is more than the value of money that has to be received at a later date.
This concept of money is based on the fact that an investor can invest the money he has received in the various options and earn some more money in the form of interest di, dividends, or capital gain after some time. If he receives the money later, he will not earn the income he would have otherwise got till the receipt of the money after a year or more. Hence, investors wish to calculate the value of money available to them at a future date.
What is the future value factor?
The future value factor (FVF) or future value interest factor (FVIF) is the equivalent value at some future date of a cash flow at time 0 or a series of cash flows that occur after an equal time interval. Simply put, the Future Value Factor or future value interest factor is used to calculate the value of a specific amount at a future date.
The Future Value Factor (FVF) is a concept used in finance to determine the future value of an investment or cash flow based on compound interest. It’s used to determine how much a current sum of money will be worth at a future date, given a specific interest rate.
The Future Value Factor (FVF) is a concept used in finance to determine the future value of an investment or cash flow based on compound interest. It helps you figure out how much a current sum of money will be worth at a future date, given a specific interest rate.
Investors use this factor to estimate the value of their money at a future date, assuming a specific interest rate. It is also used for calculating the annuity payments or annuity due. For calculating the FVF, the interest is compounded based on the period specified. It is assumed that the principal’s interest during the period for compounding will also be reinvested and earn interest. Either a formula or tables can be used for determining FVF.
FVF Formula – How to calculate future value factor?
The formula for calculating the FFV uses the interest rate in percentage
FVF = ( 1 + r)^n
where r is the interest rate in percentage for the period after which it is compounded, and n = is several periods for which the investment is compounded.
The investment’s annual interest rate should match the interest rate for each period and the number of periods when the interest is compounded.
An alternate formula for calculating the FVF uses the number of compounding periods in a year
FVF = (1+ (APR/m))^nXm
In this alternate formula, APR is the annual percentage rate for the investment, m is the number of periods in the year when the interest is compounded, and n is the total number of years. Similar formulas with some variations are used for calculating the FVF for the annuities due to the FVF Table.
Since calculating the FVF using the formula is time-consuming and tedious as it involves compounding, many investors prefer to use tables to determine the FVF for different interest rates and periods. The table is usually available for 1 to 30 periods, depending on the investment duration. Since the interest rate on debt is usually limited to 18% for most investments, the FVF corresponding to interest rates up to 18% is usually provided in the table. However, it is possible to generate tables with more periods and higher interest rates depending on the investment.
For example, if you want to determine the future value of 1000 dollars invested for five years at an annual interest rate of 5%:
Using the formula, the FVF would be: FVF = (1 + 0.05) raised to the power of 5 = 1.2769 (rounded off to four decimal places)
Then, you’d multiply the present value by the FVF: FV = 1000 dollars multiplied by 1.2769 = 1276.90 dollars
So, the future value of the 1000 dollars after five years at 5% annual interest would be 1276.90 dollars.
The FVF is a useful tool when planning for future financial needs or comparing investment opportunities.
Future value interest factor Table (FVIF Table) example :
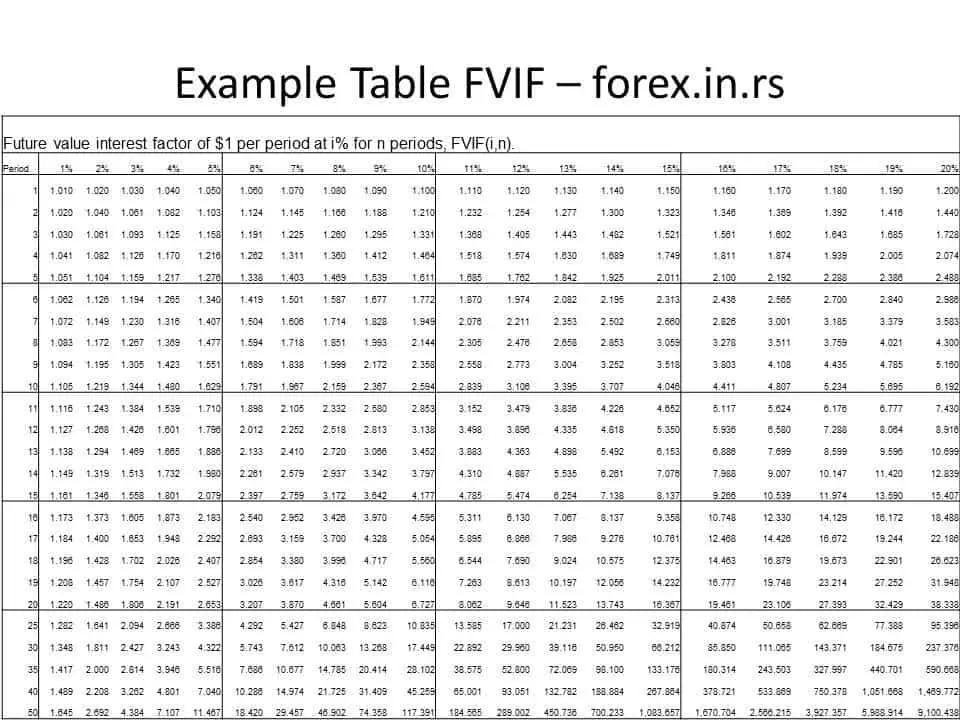
Using the table for determining the FVF is comparatively simple; the investor will only have to look at the interest rate and the compounding period. The table is also convenient since the investor can easily compare the FVF for the different periods and different interest rates to make a decision accordingly; he does not have to calculate values manually. Similar tables are also available for annuities and annuities due. Most financial consultants will use the tables while advising the investor on the options for investing their money.
Conclusion
The FVF determines the value of one dollar invested later for different interest rates and compounding periods. The factor obtained by calculation using the FVF formula or derived from the FVF table is then multiplied by the available amount. Investors can use this to choose between debt investments, which are less risky and offer low returns. Equity investments offer better returns yet may also result in losses for the investor. FVF highlights the time concept of money. A business or individual should get the payment due at the earliest to be invested instead of waiting to receive the amount and losing the interest otherwise earned.
























