Table of Contents
Establishing a Limited Liability Company, commonly known as an LLC, has proven to be an ideal choice for many traders aiming to form a company. This preference is influenced by the key advantages that LLCs offer. To begin with, the principal benefit of an LLC, as its name suggests, is the provision of limited liability protection. This legal structure ensures that the owners, referred to as members, are not personally liable for the business’s debts and liabilities. This aspect is especially critical for forex traders given the financial risks associated with trading activities.
Furthermore, LLCs offer attractive taxation flexibility. They are default classified as “pass-through” entities for taxation, implying that the company’s profits and losses are reported on the member’s tax returns, thereby avoiding the risk of double taxation frequently associated with corporations. Despite this, if it turns out to be more beneficial, an LLC can elect to be taxed as a corporation.
In terms of management, LLCs have a straightforward structure that is easier to manage than corporations, which often require adherence to numerous formalities, including a board of directors and annual meetings. An LLC, in contrast, entails fewer meeting and record-keeping requirements, providing members with ample flexibility in managing the company.
How to Open LLC for Forex Trading?
- Choosing a State: Determine which state or country you want to form your LLC. Each state has different rules, regulations, and tax obligations. Therefore, it’s crucial to research and chooses a state beneficial to your business needs. For example, in the US
- Choosing a Name: Choose a unique name for your LLC. This name should not be the same or overly similar to an existing LLC in your chosen state. You can check this via your chosen state’s Secretary of State website.
- Registered Agent: Choose a registered agent for your LLC. The agent is the person or entity that will receive legal documents for your business. This can be an individual residing in the state of formation or a business entity authorized to do business there.
- Articles of Organization: Prepare and file the Articles of Organization with your state’s Secretary of State office. This document includes information like your LLC’s name, its purpose, information about the registered agent, and how it will be managed.
- Operating Agreement: Although not required in every state, it is highly recommended to have an LLC operating agreement. This document outlines the ownership structure, member roles, and how the business will be run.
- Employer Identification Number (EIN): Apply for an Employer Identification Number (EIN) from the IRS. This is like a social security number for your business and is required for tax purposes.
- Forex Broker Account: Find a reliable and regulated forex broker that accepts accounts opened through an LLC. Research the broker’s reputation, trading platform, trading conditions, and customer service.
- Fund Your Account: Once your Forex broker has accepted the LLC account, you can fund it and start trading. Ensure that the funding method aligns with your company’s financial strategy.
- Accounting and Tax Preparation: Keep clear and accurate records of all your transactions and financial activities. Work with a professional accountant or tax expert to help prepare your taxes and ensure you comply with all the relevant laws and regulations.
- Legal and Compliance: Depending on your trading volume and size, you might need to comply with specific SEC regulations and register with the NFA (National Futures Association). It’s essential to consult with a legal advisor experienced in Forex trading businesses.
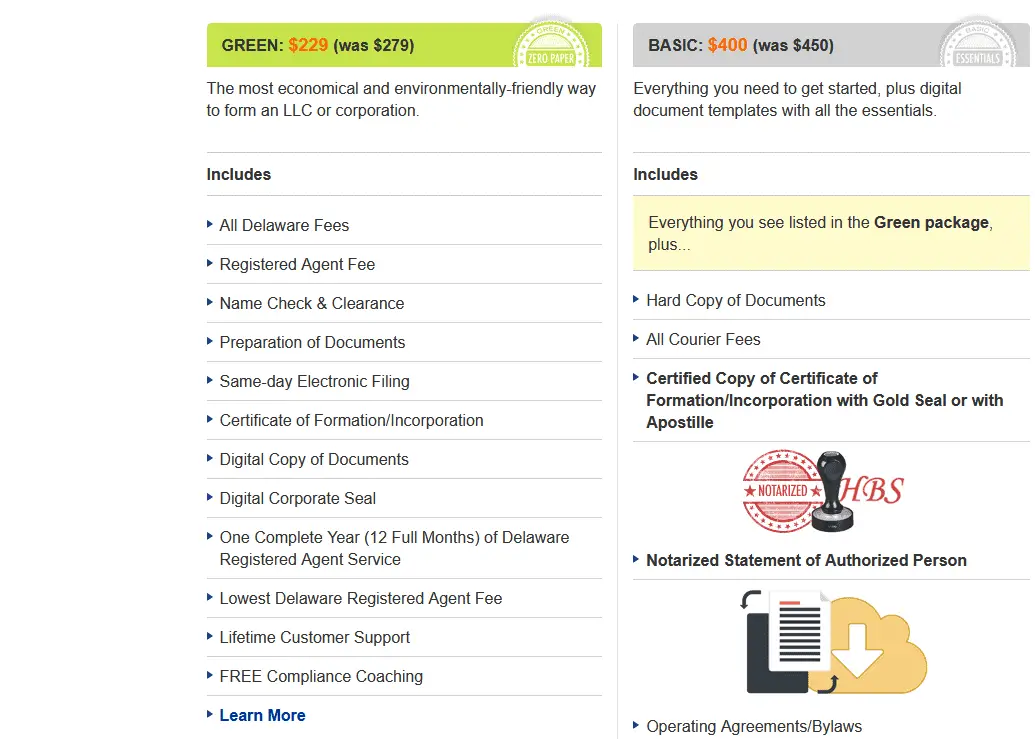
You can fill out the form and pay Dalwareinc.com; they will register your LLC forex trading company for only $229.
How to Choose a Country or State for Forex Trading LLC?
Limited Liability Companies (LLCs) are subject to various tax obligations depending on their state and country. Below are some practical examples of how this may look in different states within the U.S. and some other countries:
United States:
- Delaware: Delaware is known for its business-friendly environment and laws. No state corporate income tax on goods or services provided by Delaware corporations outside Delaware exists. The annual franchise tax is relatively low and is calculated based on shares and par value rather than profits.
- Nevada: Nevada doesn’t charge a state corporate income tax or fees on corporate shares. However, the state does require a relatively modest Business License Fee.
- California: California does impose a corporate income tax, and the state charges an annual LLC tax currently set at a flat rate of $800.
International Examples:
- United Kingdom: In the UK, an equivalent to an LLC is a Limited Company. A Limited Company pays Corporation Tax, currently at 19%. There’s also an expectation to pay employers’ National Insurance contributions if the company has employees.
- Canada: In Canada, a similar structure to an LLC would be a Corporation. Canadian Corporations are subject to federal taxes of 38% on taxable income, 10.5% after federal tax reduction, and 9% after the small business deduction.
- Australia: In Australia, a similar entity to an LLC would be a Pty Ltd Company. These companies pay a flat company tax rate, which is currently 30%, or 27.5% for small businesses.
Please note that this is a simplified overview. The reality can be more complex depending on the nature of the business, and there can also be other taxes and fees, such as sales taxes, property taxes, and more. Getting advice from a tax professional or accountant is crucial to understand the total tax obligations of an LLC or equivalent entity. Also, please be aware that tax rates can change, so the rates mentioned above may not be current if you’re reading this at a later date.
Forex Trading LLC Tax Obligation by Country
Note that forex gains might be subject to different tax treatments depending on whether they’re classified as income or capital gains, and the specifics can vary significantly from country to country. Here’s a broad overview:
- United States: In the U.S., forex trading gains may be taxed either as ordinary income or as capital gains, depending on the specifics of your situation. The IRS Section 1256 contract allows 60% of forex gains to be taxed at the long-term capital gains rate and 40% at the short-term rate, no matter how long the asset was held. This could be advantageous given the lower long-term rates. However, you may also opt out of Section 1256 and have your forex gains taxed at your regular income tax rate. LLCs are generally not taxed; income “passes through” to the owners, who report it on their tax returns.
- United Kingdom: Forex trading in the UK is considered gambling by HMRC (Her Majesty’s Revenue and Customs), so any profits are not subject to capital gains tax or income tax. However, if forex trading is conducted in the context of a business (as it might be in an LLC), it could be subject to Corporation Tax, currently at 19%.
- Canada: In Canada, forex gains can be taxed as either income or capital gains, depending on the nature of the trading activity. If you’re running a business (like an LLC) that trades forex, profits will likely be taxed as income at the corporation tax rate.
- Australia: In Australia, profits from forex trading by a company would generally be taxed as ordinary income at the company tax rate.
- Germany: In Germany, corporations are subject to a tax of approximately 15%. This applies to gains from forex trading as well.
Again, this is a very simplified overview, and the actual tax situation could be much more complex, especially for a business involved in forex trading. Additional considerations might include VAT/GST, sales, business, and property taxes. It’s crucial to consult with a tax professional familiar with forex trading and the specific tax laws in your country.
Forex Trading LLC Advantages
An LLC, or Limited Liability Company, is an excellent choice for traders looking to form a company due to its advantages. Here are several key reasons:
- Limited Liability Protection: One of the most significant advantages of an LLC is, in its name – limited liability. This means that the owners (members) of the LLC are not personally responsible for the company’s debts and liabilities. Only the business assets are at risk if the LLC incurs debt or is sued. The members’ assets, such as their homes or bank accounts, are protected. This is particularly important for forex traders, as trading can be a risky venture with the potential for significant financial losses.
- Flexibility in Taxation: An LLC offers flexible tax options. By default, LLCs are treated as “pass-through” entities for tax purposes, which means that the profits and losses of the LLC “pass-through” to the individual tax returns of the members. This avoids the “double taxation” that can occur with corporations, where profits are taxed at the corporate level and again when distributed to owners as dividends. However, an LLC can also be taxed as a corporation if it’s more advantageous.
- Ease of Management: Unlike corporations, which require a board of directors, annual meetings, and other formalities, LLCs are easier to manage. They have fewer requirements for meetings and record-keeping, allowing the members a great deal of flexibility in deciding how the company will be run.
- Profit Distribution: In an LLC, profits are not distributed based on the percentage of ownership. This means that if one member contributed more capital to the business, the members could still decide to split the profits equally or in any other proportion they choose.
- Professionalism and Credibility: Forming an LLC can add credibility to a trading business. The LLC designation in your business name can make your operation appear more professional to banks, brokers, and potential partners or clients.
In summary, an LLC combines the liability protection of a corporation with the tax flexibility and ease of management of a partnership, making it an attractive choice for many forex traders. However, everyone’s situation is unique, and it’s essential to consult with a legal or financial advisor to determine the best type of business entity for your specific needs and goals.
























