Leverage is a strategic tool extensively used in various types of trading, including stocks, commodities, indices, and particularly in the forex market.
Fundamentally, Leverage involves using borrowed capital to increase the potential return on investment. It allows traders to control a large position with a small amount of capital, enhancing their buying power in the market. For instance, with a leverage of 1:50, a trader can control a $50,000 position with just $1,000 of their capital.
While the prospects of high returns can be attractive, Leverage is a double-edged sword. Just as it can multiply profits when the market moves in a trader’s favor, it can also magnify losses when the market moves against the trader, sometimes even leading to the loss of the entire trading account. Therefore, understanding Leverage and managing it is critical in the trading industry.
What Does 50:1 Leverage Mean?
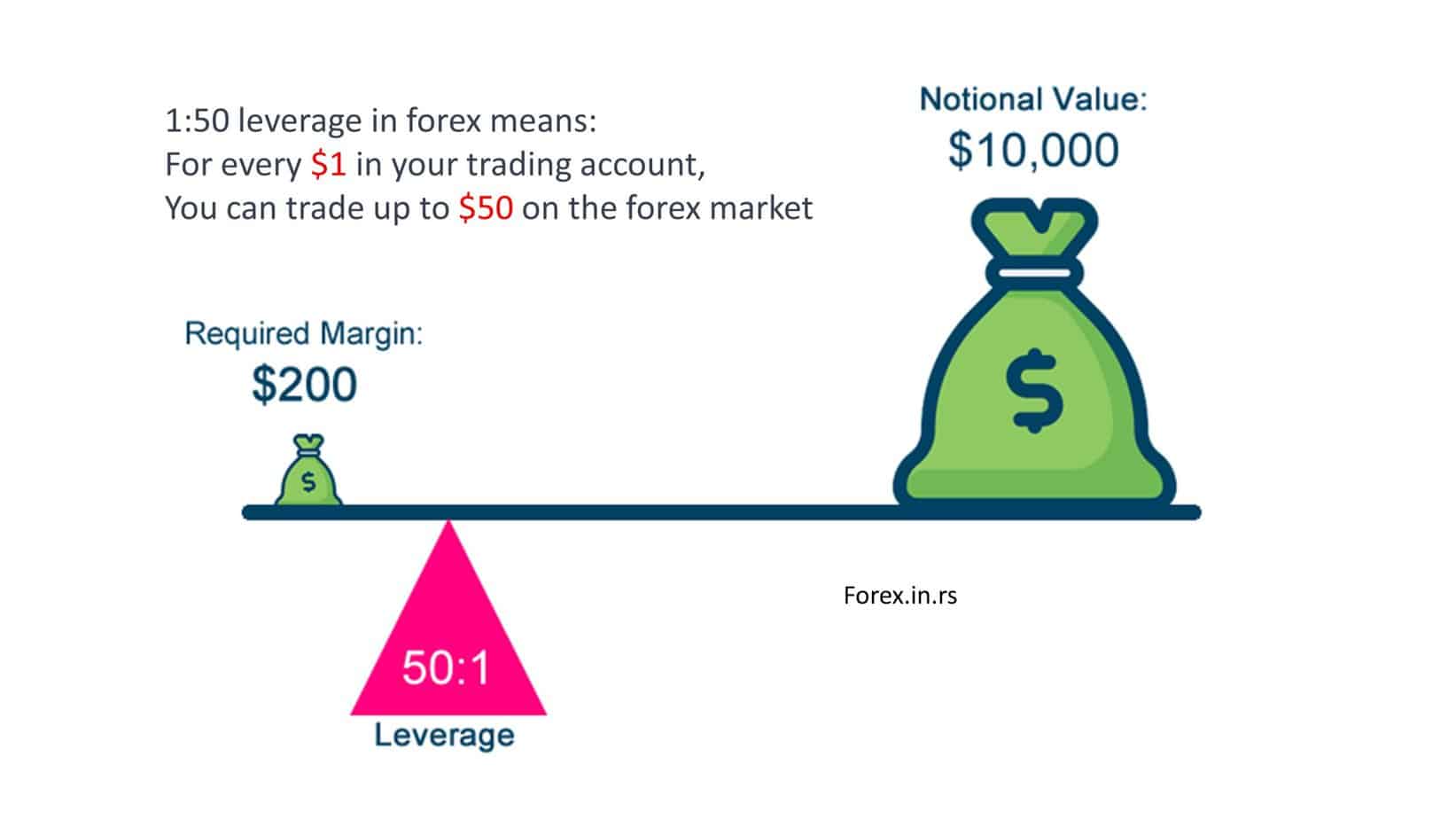
1:50 Leverage means for every $1 in your trading account, you can trade up to $50 on the forex market. For example, if you have $1000 in your trading account, with a leverage ratio 1:50, you can control and trade with $50,000 on the forex market. Remember, while this increases your potential profits, it also amplifies the potential losses you can incur.
High Leverage allows you to increase your exposure to the market, thus potentially amplifying your profits, but it also increases the risk of more significant losses.
1:50 Leverage and Trading Margin
Margin and Leverage are closely related. Margin is the amount of money needed to open a leveraged position. For a 1:50 leverage ratio, the margin requirement would be 2% of the total trade value. This is because one divided by 50 equals 0.02 or 2%. So, to trade $50,000 on the forex market using 1:50 Leverage, you’d need to have $1,000 in your account as the margin.
Let’s start with Leverage. Simply put, Leverage is the borrowed capital you use to increase your potential return on investment. In forex trading, Leverage is often expressed as a ratio. In your case, the Leverage is 1:50. For every $1 of your own money (also known as margin), you can trade $50 on the forex market. In other words, your broker allows you to amplify your trading capacity by a factor of 50.
See my video related to Leverage:
Now, let’s discuss margin. Margin is the amount of money you need to put up to open a leveraged trade. In the context of 1:50 Leverage, the margin requirement would typically be 2% of the total value of the trade (since one divided by 50 equals 0.02 or 2%). So, if you wanted to open a position worth $50,000, you would need at least $1,000 in your account. This $1,000 is your margin.
Margin acts as collateral or security deposit on the leveraged trade. If the trade moves in your favor, your profit is based on the total value of the position, not just the margin you put up. Conversely, if the trade moves against you, your losses can also be based on the total trade value. This is why trading on Leverage is often described as a double-edged sword – it can amplify your gains and losses.
For example, if you have a 1:50 Leverage and want to trade one lot (100 000 units), you will need around $2000 required margin. If you have 1:500 Leverage, you will need around $200 required margin.
In the first scenario, with 1:50 Leverage, you can trade up to 50 times your money in your account. If you want to trade one lot (i.e., $100,000), you must have $2,000 in your account. This is because $100,000 divided by 50 equals $2,000, 2% of the total trade size. This $2,000 is your margin, or the money you need to put up to open the trade.
In the second scenario, with 1:500 Leverage, you can trade up to 500 times your money in your account. If you want to trade one lot (i.e., $100,000), you only need $200 in your account. This is because $100,000 divided by 500 equals $200, 0.2% of the total trade size. This $200 is your margin for the trade.
So, as you can see, increasing your Leverage allows you to trade more prominent positions with a smaller amount of your own money. But while this can increase your potential profits, it also amplifies your potential losses. This is why it’s essential to use Leverage responsibly and ensure you have a good understanding of the risks involved.
Benefits of 1:50 Leverage
- Increased Potential Profits: The main benefit of Leverage is that it can significantly amplify potential profits. If the market moves in your favor, the percentage gains are based on the total amount of the leveraged position, not just your margin.
- Capital Efficiency: Leverage enables traders to take on more prominent positions without committing the entire capital upfront. This makes the capital in your account more efficient, potentially allowing you to make more enormous profits from a smaller investment.
Risks of 1:50 Leverage
- Increased Potential Losses: While Leverage can amplify profits, it can also amplify losses. If the market moves against you, you can lose much money, potentially more than your initial margin.
- Margin Calls: If the market moves against your position and your account value falls below the margin requirement, your broker may issue a margin call. You must deposit additional funds into your account to keep the trade open. If you can’t meet the margin call, your broker has the right to close your position, and you’re liable for any losses.
Conclusion
1:50 Leverage in forex trading offers the potential for significant profits but also significant losses. Understanding how it works and the risks involved before engaging in leveraged trading is essential. As always, prudent risk management practices can help protect your trading capital.
























