Table of Contents
In trading, supply and demand principles dictate the equilibrium price of an asset, with supply referring to the amount available and demand representing the desire to purchase. Shifts in these forces can lead to price movements, as increased demand or decreased supply typically pushes prices up, while increased supply or decreased demand generally drives prices down.
Within this realm, a ‘demand zone’ emerges as a critical tool, enabling traders to anticipate potential upward price movements. This article profoundly explains demand zones, their importance, and how they can be effectively leveraged in trading.
What is Demand Zone?
The demand zone represents the high liquidity price levels area on the trading chart where the volume of buying trades significantly exceeded selling trades. Usually, in the demand price zone, most traders close sell orders or make new buy orders.
A demand zone is a specific price range on a chart where, historically, the asset’s price tends to find support and doesn’t fall below. Simply put, it’s a region where buying interest surpasses selling pressure, leading to a potential price surge. This phenomenon can be attributed to the inherent principle of demand – as more traders want to buy an asset (demand) than sell it, its price goes up.
Let us analyze one practical example:
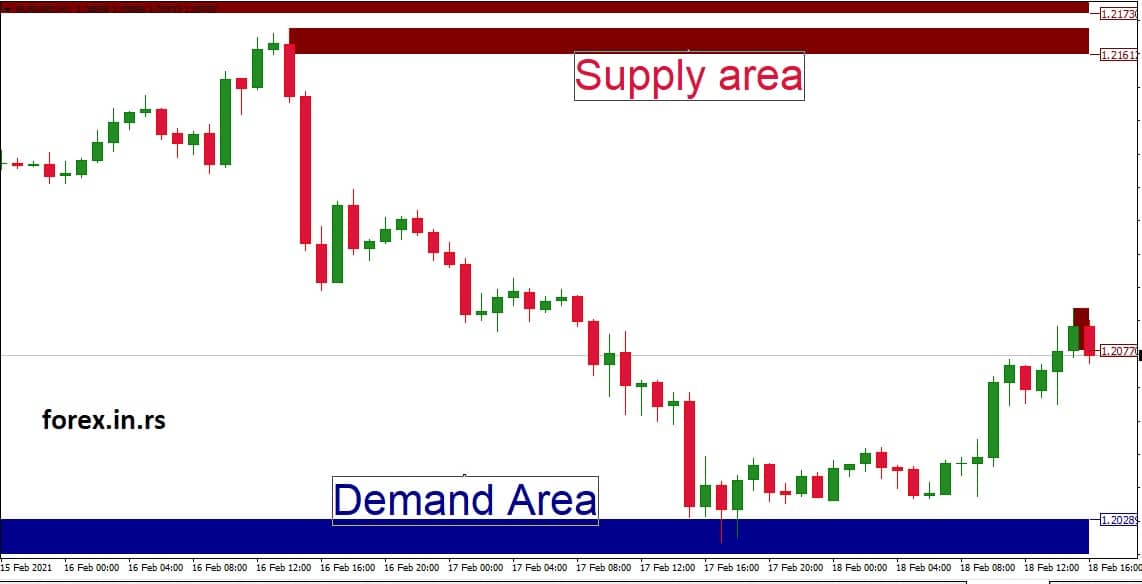
As you pore over the GBP/USD daily chart, a particular price range stands out — between 1.2016 and 1.2026. Over the past weeks, every time the currency pair touches this zone, it seems to find support and subsequently bounces upwards.
- Identification of the Zone: The zone between 1.2016 and 1.2026 has acted as a cushion for the price, preventing it from falling further multiple times. This recurring behavior earmarks this area as a demand zone, indicating substantial buying interest.
- Volume and Price Action: On scrutinizing the price actions within this zone, you observe prominent bullish candles or wicks touching down and rejecting the lower prices. Additionally, there is an increase in trading volume during these times, highlighting robust buying activity in this zone.
- Market Sentiment: On researching further, you find that this price zone might coincide with favorable news for the GBP or adverse news for the USD. Such news could bolster traders’ confidence in the pound, prompting them to buy whenever the price dips into this zone.
- Trading Strategy: Recognizing this demand zone, a trader might consider entering a long position the next time the price nears the 1.2016 to 1.2026 area, especially if there are bullish reversal signals. To manage risk, a stop loss might be set just below the zone, around 1.2005, protecting against a potential sharp decline if the zone fails.
- Outcome: In subsequent sessions, as the GBP/USD price dips into the range of 1.2016 to 1.2026, it quickly finds support and bounces back. Traders who took long positions within this zone benefit from the subsequent price appreciation, underscoring the utility of demand zones in forecasting potential price reversals.
This example emphasizes the significance of identifying demand zones in forex trading. By recognizing these pockets of heightened buying interest, traders can make strategic decisions that align with the broader market sentiment, maximizing potential gains and minimizing risks.
Characteristics of Demand Zones
- Historical Relevance: Reliable demand zones have been tested multiple times; whenever the price enters this zone, it bounces back upwards.
- Volume Surge: A significant increase in buying volume often accompanies the price when it reaches the demand zone. This surge indicates strong buying interest.
- Clear Boundaries: The best demand zones have clear boundaries, making it easier for traders to identify entry and exit points.
Why Are Demand Zones Important?
- Price Prediction: Recognizing demand zones can provide insights into potential price movements, offering traders a strategic edge.
- Risk Management: Setting stop losses just below a demand zone can help limit potential losses while taking advantage of the price bounce within the zone.
- Strategy Formulation: Demand zones provide traders with critical areas to monitor, aiding in formulating buying strategies.
Identifying Demand Zones
To identify a demand zone:
- Analyze Historical Price Action: Look for areas where the price has bounced upwards multiple times.
- Monitor Volume: Seek areas where volume spikes as the price enters the zone.
- Utilize Technical Indicators: Tools like the RSI (Relative Strength Index) can help validate demand zones, especially when the RSI indicates oversold conditions.
Trading Using Demand Zones
Once a demand zone is identified:
- Wait for Price Retest: Before moving, wait for the price to re-enter the demand zone and show signs of a bounce.
- Set Stop Losses: To manage risk, set a stop loss slightly below the identified demand zone.
- Monitor Closely: Stay vigilant. Market conditions can change, and demand zones may not always hold.
You can check three examples from our article:
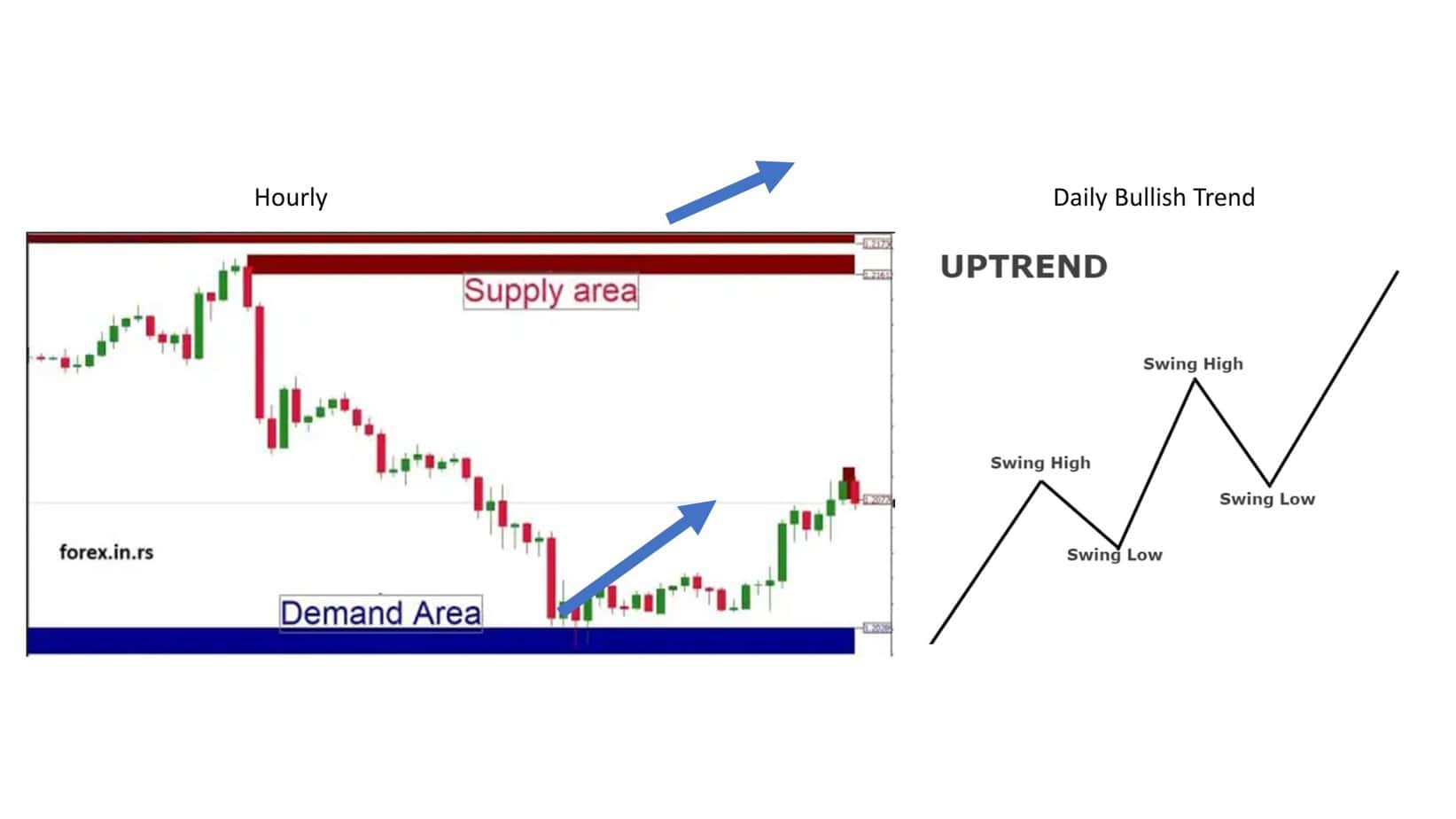
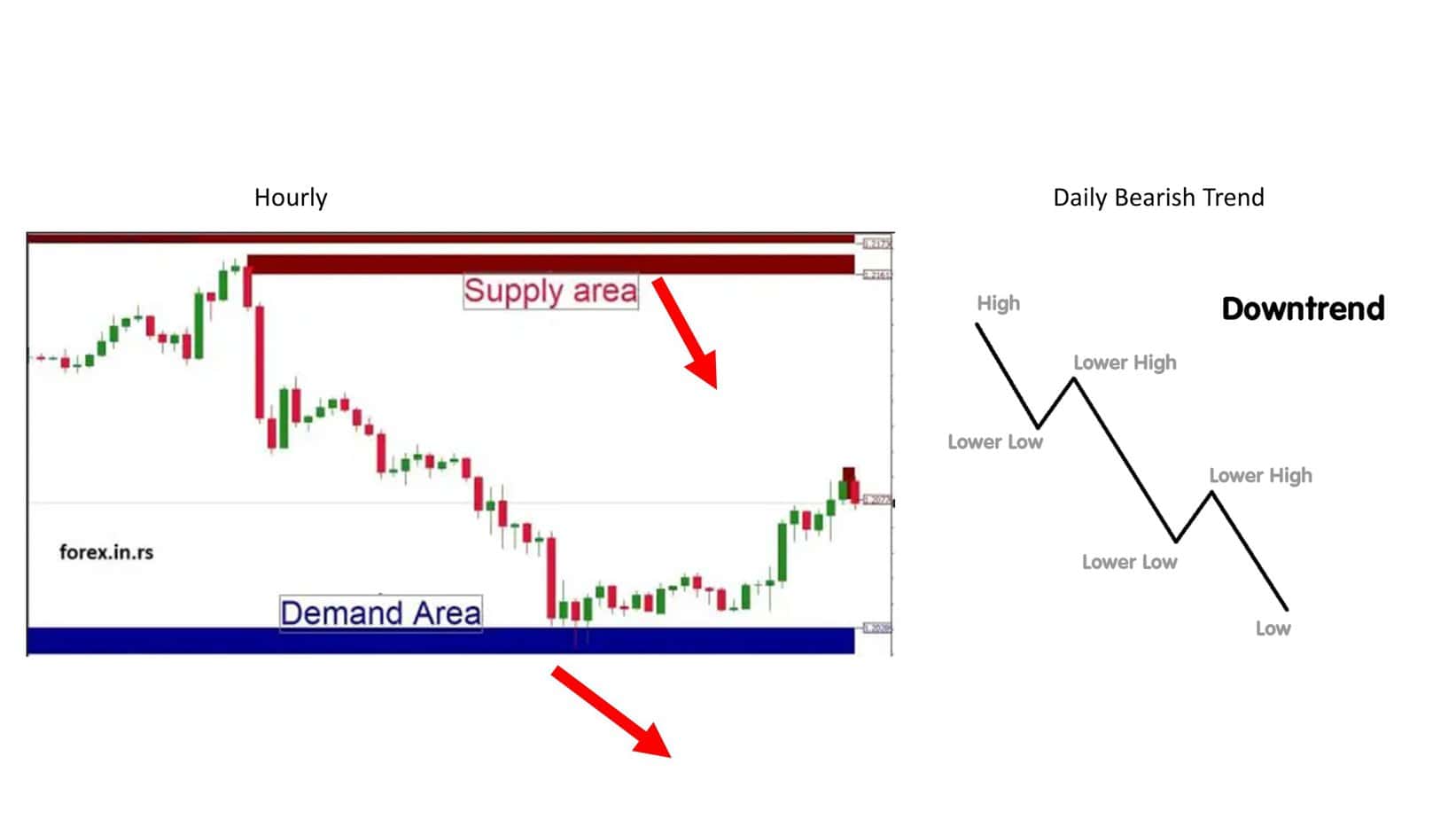
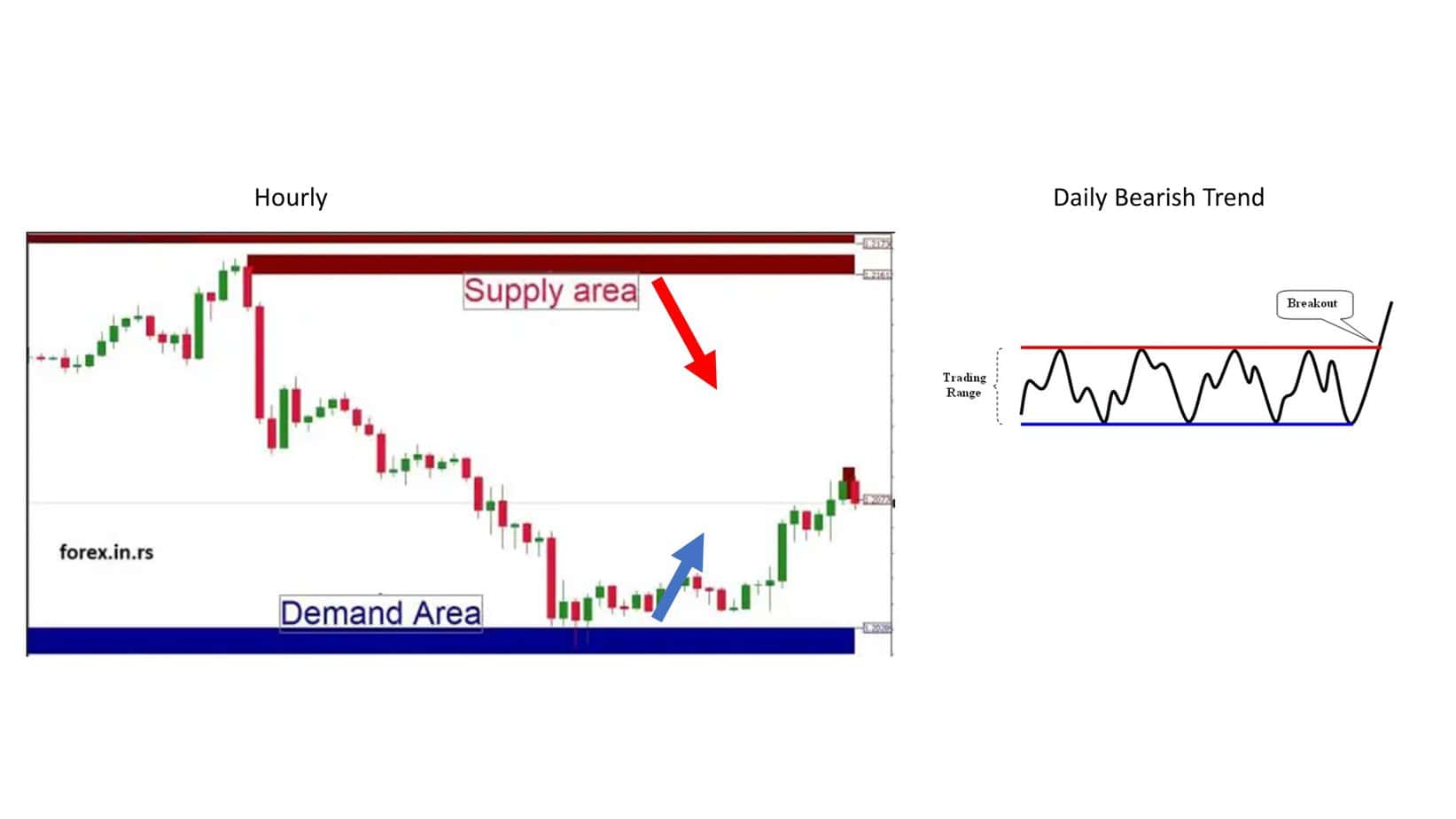
Please read our full article on how to trade supply and demand zones.
Potential Pitfalls:
It’s crucial to note that while demand zones offer valuable insights, they aren’t foolproof. Many external factors, including geopolitical events, economic data releases, and changes in market sentiment, can influence markets. Combining the insights gained from demand zones with other technical and fundamental analyses is always advisable.
Conclusion
Demand zones are an integral part of the trader’s analytical toolkit, offering insights into areas of strong buying interest. By understanding, identifying, and skillfully leveraging these zones, traders can enhance their strategic decision-making, optimize entry points, and better manage risks. However, as with all trading tools, demand zones should be used judiciously and with a broader analytical framework.








