Since its inspection in 1867, Forex trading has intrigued many traders. In addition to being a volatile tradable asset, the charm of exchanging foreign currencies seems to grow stronger with time. According to the reports released by the Bank of International settlements, approximately $5.1 trillion Forex is traded daily.
Generally, we exchange currencies for several reasons like tourism, education, commerce, and more, but how is currency trading different, and is it for you? Let’s explore these questions in this article.
What is forex trading?
Forex trading is the conversion of one national currency into another to make a profit. Forex trading involves buying and selling currency pairs and can be defined as buying one currency, and another’s simultaneous selling.
Now the next thing that we need to define is the forex market.
What is the forex market?
The forex market is a global marketplace for exchanging national currencies against one another, including banks, funds, trading companies, and individuals.
The place where this exchange takes place is known as the Forex market. You might not be aware of it, but every single person is affected by currencies. Currencies are required for all imports and exports. Let’s assume that you are a connoisseur of French cheese, but you live in the USA. To get cheese from France, someone has to pay the French retailer in Euros. It could be a company, you, or anyone making the purchase. This means that Euros will be bought with an equivalent value of USD to import cheese. Similarly, if a French man wishes to buy Indian cotton, he will have to pay in INR. And, the trail will go on.
Coming back to the Forex market, you must know that it is unlike other trading markets as it lacks a central marketplace for the exchange to take place. All the exchanges happen over-the-counter or OTC electronically. This means that traders make all the transactions via computer networks. Since there is no central place for exchange and transactions happen virtually, this market operates 24/7 for five full days and one-half day for a week. There are no boundaries in this market. The trade is worldwide, with London, Tokyo, Frankfurt, Singapore, Sydney, New York, Zurich, Hong Kong, and Paris being major financial centers globally. These places cover almost all the different time zones. As a trading day ends in Hong Kong or Tokyo, another trading day begins in New York. This is why this market is bustling all the time.
Forex history
The stock exchange is believed to have begun in the early 16th century and was established in 1611. Compared to that, the Forex market is relatively new. Yes, countries have been exchanging currencies since they started minting the, but it hasn’t been long since the market was properly established and regulated. In 1971, after the Bretton Woods agreement, an increased number of currencies could float freely and could be exchanged. You can read more details in our forex history article.
The modern forex market was established in December 1971. when The Smithsonian Agreement was announced. In 1971, a new dollar standard was created whereby several industrialized states’ currencies were pegged to the US dollar. U.S. dollars were no longer backed and exchanged for gold.
The value of currencies has always varied. This makes it volatile, thus, giving birth to the need for trading and exchange services. Most of the Forex trading is conducted by investment and commercial banks. They represent their clients. There are good opportunities for small and individual traders are well.
Spot, Forwards, and Futures Markets
Big corporations, institutions, and small traders trade Forex in three ways. The first one is in the spot market. It is one of the most popular ways trade is made because the other two markets, the futures, and the forwards market, use it as their underlying asset. Earlier, the futures market was the most popular because it allowed individual traders to hold a position for a more extended period. The spot market was able to shadow the futures market because of technological advancements. Now individual traders have access to numerous Forex brokers, and they can easily keep an eye on their investments through the trading portals offered to them by their brokers.
Generally, when someone says Forex market, by default, they are talking about the spot market. Its two counterparts are more popular among larger institutions as they look forward to hedging their risks out to a later date in the future.
Another major difference amongst these markets is that the current prices are used for buying and selling currencies in the spot market. This price, determined by demand and supply, tells traders about several things, like a country’s economic performance, current interest rate, and local and global sentiments towards an ongoing political situation. Since these are the key fundamental factors, traders can assess the future price movements using these current rates or how one currency will perform against them. The deals made in this market are called spot deals. These deals are bilateral in nature. Here, one party a currency is delivered by one party to the other on an agreed-upon amount to the other party. In exchange, the first party receives another currency of a specified amount at a pre-discussed exchange rate.
Once the position gets closed, cash is used for settlement. Despite the spot market being famous for transactions happening in the present rather than the future, it can take around two days to complete one transaction.
Instead of trading the actual currencies, deals are made in contracts in the futures and forwards markets. These deals claim to a certain type of currency, a future settlement date, and a defined per unit price.
Two parties trade contracts over the counter in the forwards market. The party settles all the terms of trade.
The futures market operates differently as futures contracts are traded based on a standard size and a settled date. This market is regulated by the National Futures Association in the United States. Futures contracts are more specific in nature. They have details like how many units have been traded, the delivery and settlement dates, the minimum increment in price, and more. These details are not customizable. The exchange offers clearance and settlement to traders.
Both futures and forwards are binding. They are also settled for cash upon expiry. It’s important to know that contracts can be bought or sold before the expiry date. Both markets offer protection against the risk involved in currency trading.
Forex and Hedging
The value of currencies fluctuates continuously. This becomes difficult for companies that do business overseas to limit their risk. When they are buying or selling goods outside of their native countries, it biomes easier if the value of the currency stays put. There is a way to hedge this currency risk that is offered by the Forex markets. An exchange rate is fixed, and this will be used for the transactions.
Hedging is possible by buying or selling currencies in advance in either the forward market or the swap market. These markets lock the exchange rate.
Currency value fluctuation is avoidable when only personal utilities are bought, but even a pip value change can disturb the books of a large-scale transaction. Consider this example. Suppose that a US-based company is planning to sell locally produced blenders in the European markets. The company begins trading when the EUR/USD exchange rate is €1 to $1. Let’s assume that, to the manufacturer, one blender costs $100. The company decides to sell it for €150 in the European market. Ideally, the company will make $50 on every blender sold in Europe because both the currencies have equal values in this example. In a turn of events, the dollar’s value begins to appreciate against the euro, and the exchange rate becomes 0.80. This means that $0.80 is required to purchase €1.
While appreciation of your native currency is a good thing, it will be problematic for this company because their manufacturing cost will remain the same, that is $100, but the selling price will depreciate. Now €150 is equivalent to $120. The company will lose a profit of $30 on every blender sold. With the strengthening of the dollar, the company’s profit margin shrank.
To reduce this risk, the company should have shorted the Euro and bought the USD when both the currencies were parity. This would have allowed the company to maintain profits even when the dollar appreciated.
The futures market allows this kind of currency hedging. The main advantage of trading in this market is that the central authority makes sure that the contracts are clear in terms and standardized. The main difference between futures and forwards is that the latter is more liquid as the former contracts are decentralized. Futures contracts also exist within an inter-banking system globally.
Forex volatility
Forex volatility is the measure of overall price fluctuations over a certain time, how rapidly a market’s prices change in the forex market. It is merely the standard deviation of returns.
The forex market is volatile because several factors can affect a currency’s value other than the technical ones. These factors are called fundamental factors. They cover a whole range of powerful influencers like the interest rate, GDP, tourism, trade flow, economic strength, and a country’s geopolitical stability. These factors are important as they affect the demand and supply of a currency, thus, creating everyday volatility. Traders stand to profit when the value of the currency increases or decreases compared to the other one. While speculating, you must also look at both the currencies of your currency pair. A decrease in the value of one currency means a rise in the value of the other currency.
Let’s see how you can make speculations with this example. Suppose a trader expects that the USA’s interest rates will rise compared to those prevailing in Australia, keeping the 0.71 as the exchange rate between the pair AUD/USD (AUD 1.00 = USD 0.71). If what this trader is hoping for happens, the American dollar demand will rise, subsequently leading to the fall in the two currencies’ exchange rate as now you need fewer USDs to one AUD.
Let’s assume that with the rise in the interest rate, the exchange rate has fallen to 0.50 (AUD 1.00 = USD 0.50). Now you need USD 0.21 less to buy one AUD. If the trader had trusted his speculations and went short on AUD and long of USD, he would have profited from this interest rate fluctuation. This is how you can use other factors to make speculations as well.
Currency: an Asset Class
Currencies act as an asset class in two different ways:
- It allows you to earn the differential interest rate that exists between two currencies.
- Profit could be made by leveraging the exchange rate.
It is quite straightforward to profit from the difference in the interest rates of the two currencies. An investor can buy the one that offers a higher rate of interest and short the other one. Before the financial crisis of 2008, traders would buy GBP and short JPY because GBP offered a much higher interest rate.
How is Currency Trading Possible
Trading, in general, was difficult for small and individual traders before the internet, Forex trading more so. Before the internet made Forex trading accessible to everyone, the market was dominated by hedge funds, multinational corporations, and some individuals with high net worths. The market was exclusive because it demanded a huge investment in terms of capital. The Internet turned it into a retail market that aimed at individual traders. They could access the forex markets without large investment requirements as banks or brokers represented them. Traders also get high leverage from brokers that they can use to make larger profits using smaller deposits.
Forex risk management
Forex risk management represents a process that allows currency traders to minimize losses resulting from forex exchange rate fluctuations. Forex risk management is based on the ability to protect your trading portfolio from losses. Usually, forex traders need to risk less than 2% from their account in one moment.
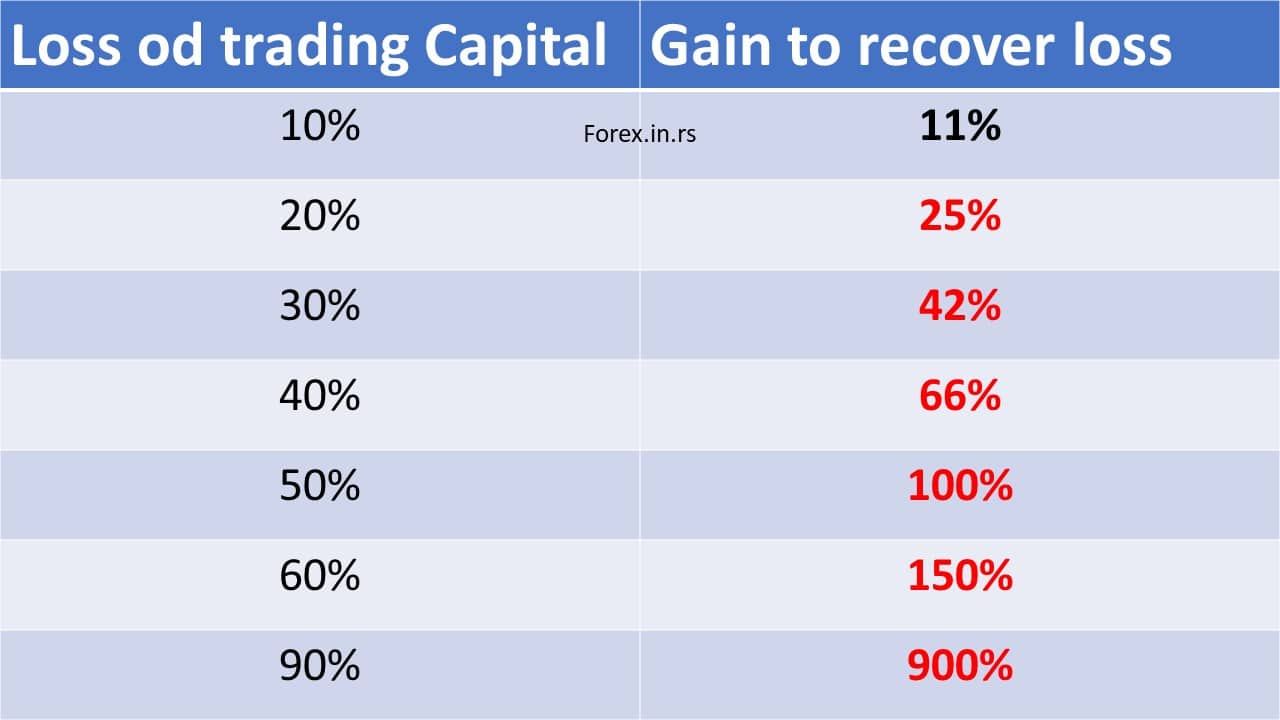
Like other trading markets, Forex is also not away from risks. Since you will be trading two currencies simultaneously, you might find the process confusing and overwhelming.
Banks across the world that trade with each other makes the interbank market. These banks are aware of the sovereign and credit risks involved, and they accept them after consideration. They try to keep themselves safe by establishing regulated internal processes. These regulations are imposed throughout the industry so that every participating bank is protected.
All the participating banks in this interbank market offer bids for the currency of their choice, making supply and demand the mechanism on which it runs. The trade flows are quite large, making it nearly impossible for rogue traders in the system to influence the prices in any way. The system is well-defined and helps in creating transparency.
Small retailers generally trade with small or semi-regulated brokers or dealers. This can increase the risk as these dealers do re-quote prices. They are not above trading against their customers as well. It is better to trade with a dealer that operates from a region where forex is regulated, as this will offer some degree of protection. On a general note, Forex rules and regulations are inconsistent throughout the world.
Dealers from the UK and the US are required to a comparatively more strict code of conduct. If you are planning to trade Forex, it would be good to look for regulated brokers from these two regions.
Forex Trading Pros and Challenges
Pro: Talking about daily trading volume, the Forex market is up-and-coming. Since the maximum number of transactions happens in this market, there is more liquidity here, making it easier for traders to enter or leave a trade.
Challenge: Brokers and dealers often offer high leverage to their clients. It can even go higher than 100:1. At the same time, it is undoubtedly beneficial when your speculations are right, but it can leave you in debt if you are wrong. One must understand the challenges involved with leverage before employing them.
Pro: The market operates without a break for five days a week. The day starts with Australia and ends in New York. The most important trading centers like Hong Kong, Tokyo, Paris, Frankfurt, London, and Singapore and New York and Sydney cover all the time zones.
Challenge: Forex trading is different as several indicators and economic fundamentals influence currencies’ values. A trader must learn to see the bigger picture if they hope for their speculations to be productive.
Conclusion
If a trader wants to begin trading with smaller capital, then the Forex market will be up-and-coming for them. They can make a significant profit with their limited funds by doing swing trading or day trading. If you wish to invest a larger sum in the market, consider long-term trading based on fundamental analysis. A carry trade can be beneficial too. To be a successful Forex trader, one must consider both fundamental and technical analysis.
























