Table of Contents
The foreign exchange market, or Forex, is a global marketplace for buying and selling national currencies against one another. It operates 24 hours a day, five days a week, through a decentralized network of banks, brokers, and financial institutions. Forex trading involves exchanging currencies in pairs to profit from fluctuations in exchange rates.
Understanding forex trading in simple words:
Forex or foreign exchange is the conversion of one currency to another. For example, if you have US dollars (USD) and want to convert them into Euros (EUR), you will sell them in USD or buy them in EUR. If you have EUR and want to convert it into USD, you would sell EUR or buy USD. You participate in global forex trading whenever you exchange your currency for foreign currency or vice versa. The foreign exchange market is a global decentralized market for buying, selling, and exchanging currencies at current or determined prices.
The Forex market enables the exchange of currencies between buyers and sellers through a decentralized network of financial institutions, brokers, and individual traders. Transactions occur in currency pairs, where one currency is bought and another is sold simultaneously, with prices determined by supply and demand, economic factors, and geopolitical events. Traders and institutions engage in various types of trades, including spot transactions, forwards, futures, and options, aiming to profit from exchange rate fluctuations or hedge against currency risk.
Forex, short for “foreign exchange,” refers to the global marketplace for trading national currencies against one another. It’s the world’s largest and most liquid financial market, with a daily trading volume exceeding $6 trillion as of 2024. Here’s a detailed breakdown of what Forex entails:
1. Basic Concept
- Currency Pairs: In Forex, currencies are traded in pairs (e.g., EUR/USD, GBP/JPY). Each pair consists of a base currency and a quote currency. When you trade a pair, you buy one currency and sell the other simultaneously. For example, if you trade EUR/USD, you buy euros (EUR) and sell US dollars (USD).
- Exchange Rate: The exchange rate is the price of one currency in terms of another. It fluctuates based on market conditions, economic indicators, geopolitical events, and other factors.
2. Market Participants
- Banks and Financial Institutions: Major banks and financial institutions are significant players in the Forex market, conducting trades for themselves and their clients.
- Corporations: Companies involved in international trade use Forex to hedge against currency risk or to manage their foreign exchange needs.
- Governments and Central Banks: Governments and central banks might intervene in Forex markets to stabilize or increase the value of their currency.
- Retail Traders: Individual traders and investors participate in Forex trading through online brokers and platforms.
3. Market Structure
- Decentralized Market: Unlike stock exchanges, Forex doesn’t have a centralized location. It operates electronically over-the-counter (OTC) through a network of banks, brokers, and financial institutions.
- 24-Hour Market: Forex trading occurs 24 hours a day, five days a week, opening in Sydney and closing in New York. This continuous operation is due to the global nature of the market and the overlap of trading hours in different financial centers.
4. Trading Mechanisms
- Spot Market: The spot market involves the immediate exchange of currencies at the current exchange rate. Trades are settled “on the spot” or within two business days.
- Forward Market: In forward contracts, traders agree to exchange currencies at a predetermined rate on a future date. This allows them to hedge against future currency fluctuations.
- Futures Market: Similar to forwards, futures contracts are standardized and traded on exchanges. They obligate the buyer to purchase and the seller to sell a specific amount of currency at a future date.
- Options Market: Currency options give traders the right, but not the obligation, to exchange currencies at a specific rate before a certain date.
5. Trading Strategies
- Technical Analysis: Traders use charts, patterns, and technical indicators to predict future price movements based on past data.
- Fundamental Analysis: This approach involves analyzing economic indicators, political events, and other factors to determine currency value.
- Scalping: This strategy involves making small, quick trades to capture small price movements.
- Swing Trading: Traders hold positions for several days or weeks to capitalize on expected price swings.
- Day Trading: Traders open and close positions within the same trading day to profit from short-term market movements.
6. Risk and Leverage
- Leverage: Forex trading often involves significant leverage, allowing traders to control prominent positions with relatively little capital. While leverage can amplify profits, it also increases the risk of substantial losses.
- Risk Management: Effective risk management strategies are crucial in Forex trading to protect against significant losses. This includes using stop-loss orders, managing position sizes, and diversifying trades.
7. Regulation and Ethics
- Regulation: The Forex market is less regulated than other financial markets, which can lead to concerns about fraud and market manipulation. Traders should choose reputable brokers regulated by financial authorities in their respective countries.
- Ethical Trading: Traders should be aware of ethical considerations, including avoiding manipulative practices and ensuring they operate within legal frameworks.
Forex trading requires a good understanding of the market dynamics, strategies, and risk management techniques. It’s accessible to professional and retail traders, making it a diverse and dynamic financial arena.
In the context of global Forex trade, the demand for a currency concerning other currencies would always go up or down. Forex is a heavily traded market because people, businesses, and even countries participate in Forex trading. The change in the currency price may not be substantial, but there is a constant upward and downward movement in their prices. This forms the basis of online Forex trading, where a live chat on your computer screen tracks the price movements of major currencies. Here, you can buy and sell foreign currencies and market profit in a 24×7 online trading environment. This is called Forex trading.
Below is an example of a Forex price chart:
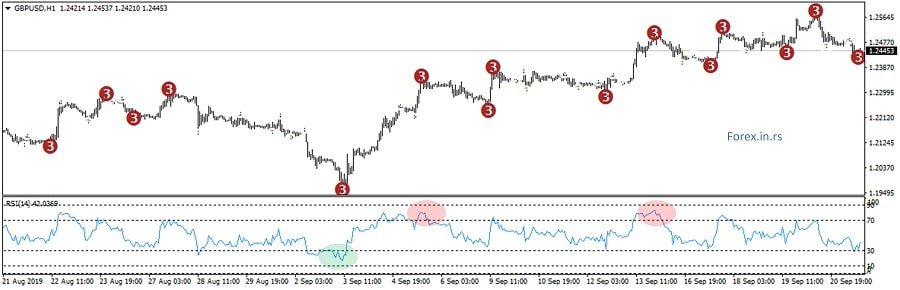
What to know about Forex?
Currency Pairs
By now, you must have understood that in Forex trading, two currencies are always involved; they are called pairs.
As currencies are traded 24 hours around the globe, the price of a currency pair keeps fluctuating.

Market Pricing
To understand how to calculate your profit in a market where the price change occurs in the 3rd and 4th decimal places, you must know how the industry works with such minor changes. Typically, a currency pair will change from 50 to 150 pips, sometimes even more or less. Pip is the short form of Point in Percentage and denotes the 4th decimal place in a currency pair’s price. In the case of the Japanese Yen, it will indicate the 2nd decimal place. When EUR/USD changes from 1.3 to 1.31, the movement is 100 pips. If you bought and sold EUR at that rate, you have made a profit of 100 pips. Subject to the number of units involved in the trade, your profit could be $10 for 1,000 units, $1000 for 10,000 units, and $1000 for 100,000 units. Learn more about pips in trading and how to calculate pip value.
Using a demo account
For a better understanding of what pairs signify, how price movements take place, how trading is done, and how profit is earned and transferred to your bank account, work with a demo account (download for free mt4 demo platform to practice trading), also called a paper account, is a good idea. Most online Forex trading platforms offer demo accounts for beginners to learn the basics of the trade before they can start full-fledged trading. It would help if you used the opportunity to improve your forex trade knowledge and hone your trading skills.
Final Thoughts
What is forex trading? Forex trading is a prevalent form of trading, and unlike others, learning the basics of the trade is not complicated. On this website, you can read everything you need about forex trading.
























