Table of Contents
At their core, companies are entities established to engage in commercial, industrial, or professional activities, aiming to generate profits for their owners or shareholders. When a company decides to “go public,” it issues shares that represent partial ownership in the company. These shares are then traded on stock exchanges, allowing individuals and institutional investors to buy and sell ownership stakes in the company.
What is the share price in stocks?
A share price represents the cost of one share in a company, fluctuating with market conditions, economic performance, and corporate health. Share price, the amount that would cost to buy one share in a company, embodies investor sentiment and valuation changes, offering both profit and loss risks.
But we need to clear this:
“Stock” denotes the holder’s part-ownership in one or several companies, indicating a broader investment portfolio, whereas “share” specifies a single unit of ownership within a particular company, highlighting the precise stake an investor holds.
A share price – or a stock price – is the amount it would cost to purchase one company share. This price is not static; it fluctuates based on various market conditions, including supply and demand dynamics, the overall performance of the economy, and the financial health and prospects of the company itself. Generally, if a company is perceived to be performing well, with solid earnings reports, innovative products, or favorable market conditions, its share price is likely to increase. Conversely, if the company faces declining profits, legal issues, or negative market sentiment, its share price may fall.
Is the share price the same as the stock price?
Yes, share price or stock price refers to the same thing. However, the difference is only in syntax because a share is the smallest denomination of a company’s stock.
Share prices reflect collective investor sentiment, and a company’s valuation can change rapidly based on new information or shifts in market trends. This fluidity makes investing in stocks an opportunity for significant gains and a risk of potential losses. As such, investors and financial analysts study companies, market conditions, and economic indicators to make informed decisions about buying, holding, or selling shares.
How share prices are determined?
The forces of supply and demand determine share prices in the market. Prices fluctuate based on investor perceptions of a company’s value and prospects. Market conditions, news, economic indicators, and company performance are key factors that influence these investor decisions, driving share prices up or down.
- Initial Pricing: Share prices are determined during a company’s Initial Public Offering (IPO) based on the supply and demand for the company’s stock, with a book-runner setting the price.
- Post-IPO Fluctuations: Share prices fluctuate after the IPO based on market supply and demand changes.
- Increase in Supply: An increase in the number of shares available, without a matching increase in demand, typically lowers the share price.
- Decrease in Demand: If the supply remains unchanged, a decrease in demand for the shares, perhaps due to changes in company leadership or poor performance, will likely lower the share price.
- External Influences: Share prices are also influenced by external factors such as:
- Industry News: Both expected and unexpected news related to the industry can affect a company’s stock price.
- Macroeconomic Data: Releases of economic data can impact investor perception and, thus, share prices.
- Political Announcements: Political events and announcements can lead to market uncertainty or confidence, influencing share prices.
Analyzing share prices involves two primary methodologies: technical analysis and fundamental analysis. Both approaches offer different insights into the potential future movements of share prices, allowing investors to make informed decisions based on their investment strategies and risk tolerance.
Technical Analysis
Technical analysis is a method that involves studying historical price and volume data to forecast the future movements of share prices. This approach is based on the premise that market prices move in trends and are influenced by the market psychology reflected in historical price patterns and volumes.
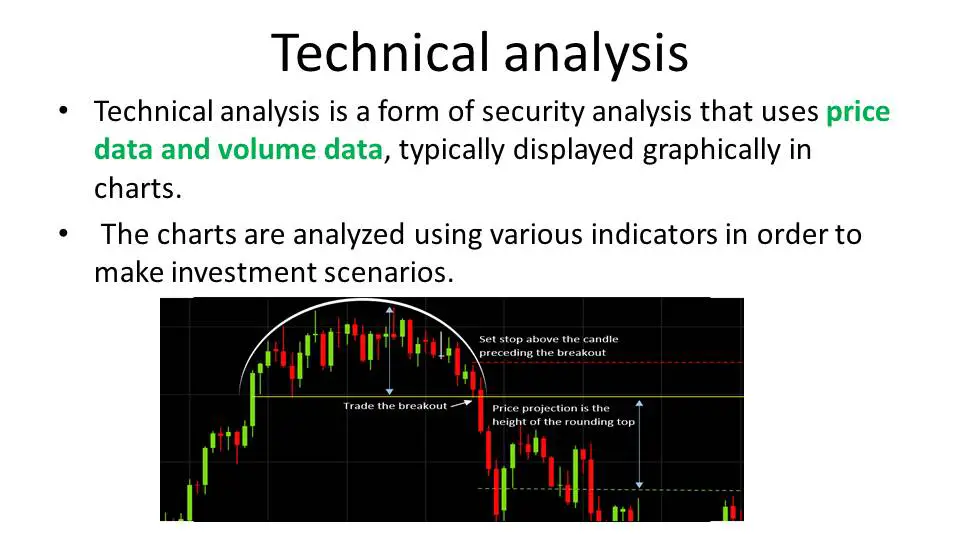
Technical analysts use tools and indicators, such as moving averages, relative strength index (RSI), Bollinger Bands, and candlestick patterns, to identify potential buying or selling opportunities. The goal is to discern patterns that suggest a stock is on the verge of a bullish (upward) or bearish (downward) trend. This method does not directly concern itself with the company’s fundamentals but focuses on price movements and trading volumes to predict future price changes.
Fundamental Analysis
Fundamental analysis takes a different approach by evaluating a company’s intrinsic value to determine whether its stock is overvalued or undervalued. This analysis delves deep into the company’s financial health, examining its income statements, balance sheets, cash flow statements, and other financial metrics such as earnings per share (EPS), price-to-earnings (P/E) ratios, and dividend yield.
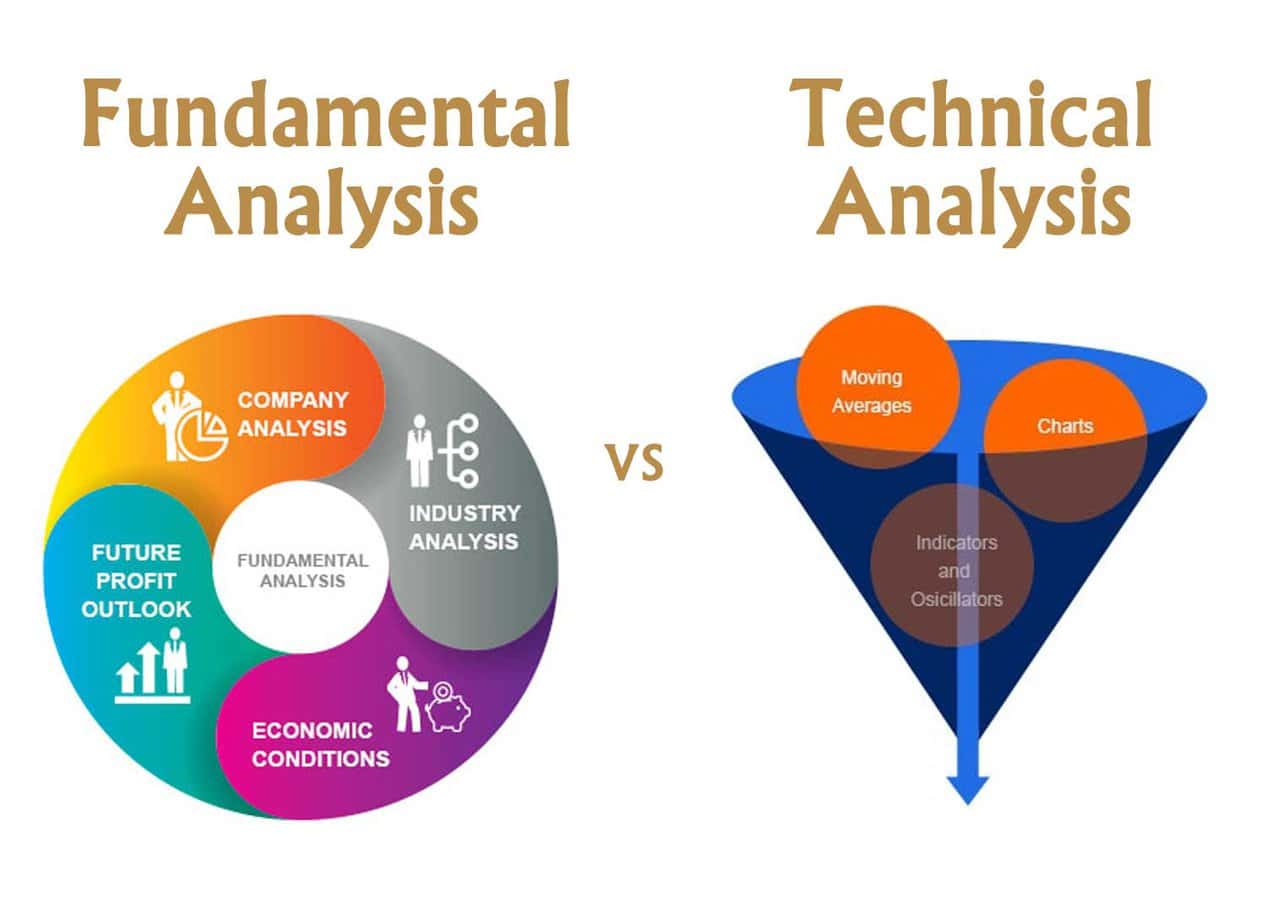
Fundamental analysts also consider the company’s competitive position, management team effectiveness, and broader macroeconomic factors like economic cycles, interest rates, and inflation. The idea is to invest in stocks priced below their intrinsic value, expecting their share price to adjust as the market recognizes their true worth.
Combining Approaches for a Holistic View
While technical analysis is often favored by short-term traders looking to capitalize on price trends and market momentum, fundamental analysis is typically the domain of long-term investors focused on the underlying business performance and economic factors. However, many successful investors combine elements of both approaches for a more holistic view of the market. By using technical analysis to time their entry and exit points and fundamental analysis to select stocks with underlying solid value, investors can enhance their potential for success in the stock market.
In conclusion, analyzing share prices is a multifaceted process requiring quantitative and qualitative assessment. Whether through the pattern-focused lens of technical analysis or the value-driven perspective of fundamental analysis, investors armed with comprehensive research and a clear strategy are better positioned to navigate the complexities of the stock market and make informed investment decisions.
A high share price is often a marker of a company’s success and stability. It enhances the company’s prestige and reputation in the market. This perception can make the company more attractive to potential investors and influence business partnerships and customer confidence. High share prices signal to the market that the company is performing well, which can have a positive feedback effect, attracting more investment and further driving up the price.
Defense Against Takeovers
A strong and rising stock price acts as a deterrent against hostile takeovers. When a company’s share price is high, acquiring control of the company becomes more expensive and less attractive to potential aggressors. This protection allows the company to pursue its long-term objectives without disrupting takeover battles.
Financial Benefits and Employee Incentives
Higher share prices can facilitate capital-raising efforts, as the company can raise more funds with fewer shares, thus avoiding excessive dilution of existing ownership. For employees, particularly those with stock options or those participating in stock purchase plans, a rising share price can be financially rewarding, enhancing employee satisfaction and loyalty. This, in turn, can improve performance and drive further growth, creating a virtuous cycle.
Dividends and Investor Attraction
Paying dividends is a tangible way of rewarding shareholders, and a rising share price coupled with consistent dividend payments can make a company’s stock more attractive to investors. This attractiveness can increase demand for the company’s shares, further supporting or increasing the share price. It also reassures current investors of the company’s health and commitment to returning value, making them more likely to hold onto their shares. This stabilizes and can drive up the share price by limiting supply.
Stock Splits as a Strategic Tool
While the primary goal is often to increase the share price, companies might strategically want their share price to be more accessible to a broader range of investors. Stock splits are a tool in this regard; by increasing the number of shares available while reducing the price per share, the company can make its shares more attractive to small investors without changing its overall market capitalization. This accessibility can lead to increased demand and, paradoxically, could eventually increase the share price.
Please read the top 15 articles explaining share price:
How to find the price per share?
What Happens to Share Price After Buyback?
What makes a share price go up?
What causes share prices to drop?
How do you calculate the share average price?
How do you calculate the share price from the Balance Sheet?
Why do stock buybacks increase share price?
Do stock splits increase share price?
Does dividend reduce share price?
How does debt affect share price?
How does issuing new shares affect share price?
How to calculate the share price of a startup company?
What happens if a share price goes to zero?
Conclusion
Share prices are a vital indicator of a company’s market perception and financial health, influencing investor confidence and corporate prestige. A rising share price can protect a company from hostile takeovers, signaling its strength and deterring potential aggressors. It also provides financial benefits, enhancing the company’s ability to raise capital efficiently and offering employees and management tangible rewards through stock-based compensation.
Dividends are crucial in attracting and retaining investors by demonstrating the company’s profitability and commitment to shareholder value. While reducing the share price, stock splits can make the stock more accessible to a broader range of investors, potentially boosting demand and, subsequently, the share price in the long term. A company’s share price reflects investors’ collective sentiment, influenced by internal performance metrics and external market conditions.
























