Table of Contents
Seeing stocks on an upward trajectory often brings a wave of excitement and optimism among traders. This happiness is not without reason; strong spikes and solid stock price trends can signal various positive developments, from breakthrough innovations and successful product launches to strong financial performance and favorable market conditions. However, seasoned traders and investors know that these moments of euphoria, brought on by surging stock prices, are often fleeting.
The reasons behind stock prices’ upward movement are as multifaceted as the market itself. Investors’ sentiment, market liquidity, and external economic indicators drive stock prices. Moreover, in the case of mutual funds, which pool investments in a diversified portfolio of stocks, the impact of stock market trends is magnified, offering both opportunities and challenges to fund managers and investors alike.
What Makes a Share Price Go Up?
The rise in stock prices is primarily driven by the fundamental principle of supply and demand: when more buyers are interested in a stock than sellers, the price goes up. This demand can be influenced by various factors, including economic indicators, corporate performance, market trends, news events, and changes in government policies, among others, which signal to investors the profit potential.
In my opinion, the intricate link between a company’s financial health and stock price is primarily anchored in how effectively it utilizes its assets and manages its profitability, as evidenced by critical metrics like Return on Assets (ROA) and Net Profit Margin (NPM). These indicators, alongside the strategic management of debt policy and the influence of company size, play pivotal roles in shaping investor perceptions and decisions, ultimately affecting the stock price.
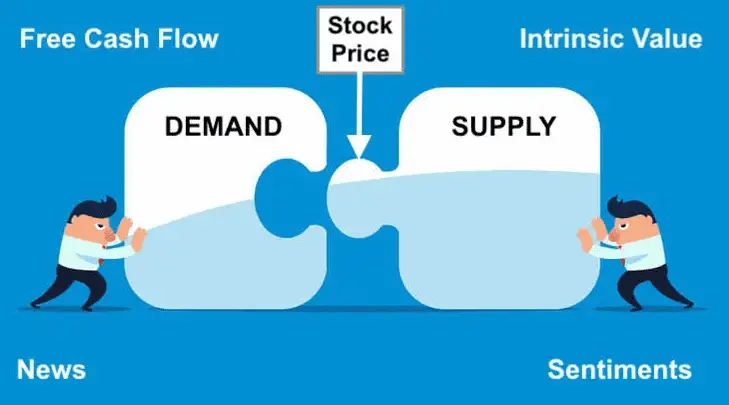
Various factors influence the price of stocks in the market, each capable of swaying market dynamics significantly. Here’s a comprehensive list of the impacts that can cause stock prices to rise or fall:
- Inflation: Rising inflation can erode purchasing power, impacting consumer spending and corporate profits. However, some sectors, like commodities, can benefit from inflationary pressures.
- Interest Rates: Changes in interest rates by central banks can influence stock prices. Lower interest rates make borrowing cheaper, potentially boosting investment and consumer spending, while higher rates may have the opposite effect.
- Corporate Performance: Earnings reports, revenue growth, profit margins, and future outlooks directly impact a company’s stock value as they reflect its financial health.
- Government Policy Changes: Policies related to taxation, trade, and industry regulations can greatly influence corporate earnings and investor sentiment, thereby affecting stock prices.
- Technological Change: Innovations and technological advancements can increase efficiency and open new revenue streams for companies, boosting their stock prices.
- Market Sentiment: The general mood or attitude of investors towards the market can drive prices. Positive sentiment can lead to higher prices, while negative sentiment can cause declines.
- GDP Growth: Indicators of economic health, like GDP growth, can signal the overall market potential for corporate earnings, influencing stock prices.
- Unemployment Rates: High unemployment rates can signal economic distress, potentially leading to decreased consumer spending and lower stock prices, whereas lower unemployment suggests economic strength.
- Incidental Transactions: Large trades by institutional investors or significant stock buybacks by companies can influence stock prices through sheer volume.
- Liquidity is the ease with which stocks can be bought or sold in the market without affecting their price. High liquidity can attract more investors, potentially driving up prices.
- Supply and Demand: Fundamental to market dynamics, the balance between available stocks and investor demand directly affects stock prices.
- Trade Wars: Tariffs and trade disputes can disrupt global supply chains, affect international sales and profits, and impact stock prices.
- Economic Policy Changes: Fiscal and monetary policies can influence economic activity, affecting corporate performance and stock prices.
- Natural Calamities: Disasters like hurricanes, earthquakes, and pandemics can cause uncertainty, disrupting supply chains and affecting stocks in various sectors differently.
- Deflation: The opposite of inflation, deflation increases the value of money but can signal weak demand, potentially leading to lower corporate earnings and stock prices.
- Exchange Rates: Fluctuations in currency values can affect multinational companies’ earnings when converted back to their home currency, influencing stock prices.
- News Events and Trends: Breaking news, both positive and negative, can quickly influence investor sentiment and stock prices. This includes corporate news, economic data releases, and global events.
- War: Conflicts and geopolitical tensions can lead to volatility, affecting industries and stocks differently. Defense and security stocks might rise, while others suffer due to uncertainty.
Inflation Impact on Stock Prices: Example with Amazon and Gold Miners
Inflation Example: Amazon
- Rising Inflation: When inflation rises, it generally erodes the purchasing power of consumers. This means people might start cutting back on non-essential purchases, which can affect companies heavily reliant on consumer spending.
- Practical Impact on Amazon: As a massive retailer, Amazon’s stock (AMZN) could face pressure under high inflation scenarios. The reasoning is straightforward: consumers may reduce their spending on Amazon’s platform with less disposable income, potentially impacting the company’s revenue and profit margins.
Inflation Example: Gold Mining Companies
- Benefiting from Inflation: On the flip side, sectors like commodities, particularly precious metals, often see an uptick during high inflation. Gold is traditionally viewed as a hedge against inflation.
- Practical Impact on Gold Miners: Companies like Newmont Corporation (NEM) or Barrick Gold Corporation (GOLD), among the world’s largest gold mining companies, may see their stock prices rise as the value of gold increases. Investors often flock to gold as a haven, boosting demand for gold and, consequently, the profitability of gold mining companies.
Interest Rates Impact on Stock Prices: Example with Tesla and Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs)
Interest Rates Example: Tesla
- Lower Interest Rates: When central banks lower interest rates, borrowing becomes cheaper. This can lead to increased consumer spending and higher investments in sectors like technology.
- Practical Impact on Tesla: Tesla (TSLA), as a technology and electric vehicle manufacturer, can benefit significantly from lower interest rates. Cheaper financing can increase consumer purchasing power, potentially boosting sales of Tesla vehicles. Lower rates make it more affordable for Tesla to borrow money for investment in new technologies and expansion projects.
Interest Rates Example: Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs)
- Higher Interest Rates: Conversely, when interest rates rise, sectors like real estate often feel the pinch. Higher borrowing costs can decrease mortgage demand and slow real estate investments.
- Practical Impact on REITs: REITs, such as Simon Property Group (SPG) or Realty Income (O), which invest in real estate and depend on financing, may see their stock prices decline with rising interest rates. Higher rates increase borrowing costs for purchasing and developing properties, potentially reducing profit margins and affecting shareholder distributions.
Corporate Performance Impacts on Stocks
Corporate performance is a critical driver of a company’s stock value, directly reflecting its financial health and operational efficiency. Let’s explore how earnings reports, revenue growth, profit margins, and future outlooks influence investor sentiment and stock prices.
Earnings Reports
Earnings reports are among any publicly traded company’s most anticipated financial updates. These reports provide a snapshot of a company’s profitability over a specific period. For example, if Apple releases a quarterly report showing higher-than-expected earnings, this positive surprise can immediately increase its stock price. Investors perceive it as a sign of strong operational performance and good management, making the stock more attractive.
Revenue Growth
Revenue growth is another vital indicator of corporate performance. It demonstrates the company’s ability to increase sales and expand its market share over time. For instance, if Amazon announces a year-over-year increase in revenue, it signals to investors that the company is growing, capturing more market share, or successfully introducing new products or services. As a result, investors might be more inclined to buy Amazon’s stock, expecting the company’s value to continue rising.
Profit Margins
Profit margins, the ratio of profits to revenues, indicate how efficiently a company converts sales into profits. A widening profit margin for a company like Nike could suggest that it is managing its costs effectively or is commanding higher prices for its products due to brand strength. Higher profit margins often attract investors, as they suggest a company can deliver more earnings from each dollar of sales, potentially leading to a higher stock price.
Future Outlooks
The future outlook of a company, including guidance provided by management about expected future earnings, revenue, and growth opportunities, plays a crucial role in shaping investor expectations. Suppose Tesla announces it expects to significantly increase vehicle production and sales in the coming years. In that case, it reflects confidence from the management and can excite investors about the company’s growth trajectory. This forward-looking information can increase investor confidence and a higher stock valuation as market participants price in the anticipated growth.
The discussion around corporate performance and its impact on stock prices centers on the principle that a company’s financial health is a critical determinant of its stock value. This relationship is underscored by several key financial metrics, which investors and analysts closely monitor to assess a company’s potential for growth and profitability.
Key Financial Metrics and Their Impact on Stock Prices
- Return on Assets (ROA): ROA measures how effectively a company uses its assets to generate earnings. A high ROA indicates efficient management and strong operational performance, making the company more attractive to investors. This attractiveness can increase the stock price, signaling the company’s ability to generate more profits with fewer investments. Conversely, a low ROA may deter investors, suggesting inefficiency in utilizing assets to produce earnings.
- Net Profit Margin (NPM): NPM measures how much net income a company earns as a percentage of its revenue. It is a crucial indicator of the company’s profitability. A high NPM suggests that the company is good at converting revenue into actual profit, which is a positive signal for investors. The implication of a high NPM on stock prices is direct; it indicates that the company has a solid potential to increase firm value, making its stock more desirable.
- Debt Policy and Capital Structure: The company’s approach to debt and equity financing significantly influences its financial performance and, by extension, its stock price. While a certain level of debt can be beneficial by allowing for tax deductions on interest payments and leveraging to increase profits, a heavy debt load can be a concern. High debt levels increase financial risk due to the obligation of interest payments, potentially reducing net profit and investor confidence. Therefore, the balance between debt and equity in a company’s capital structure can have a nuanced effect on stock prices, depending on the market’s perception of the company’s financial stability and growth prospects.
- Size of the Company: A company’s size, often measured by its assets, market capitalization, or revenue, can also impact its stock price. Larger companies are typically perceived as more stable and capable of generating consistent profits, leading to higher dividend yields for investors. This perception can increase investor confidence and drive up the stock price. However, the relationship between company size and stock performance is not linear and can vary based on industry dynamics and market conditions.
The Role of Financial Analysis
Investors perform fundamental analysis using these and other financial metrics to decide whether to buy, hold, or sell a stock. This analysis helps them gauge the company’s current financial health and its potential for future growth. The decision-making process is influenced by the company’s historical performance, comparative position within the industry, and future outlook based on current financial health.
Conclusion
The intricate relationship between a company’s financial performance and stock price underscores the importance of thorough financial analysis. By understanding how metrics like ROA, NPM, debt policy, and company size affect a company’s valuation, investors can make more informed decisions. This dynamic also highlights the significance of corporate performance in attracting investment and supporting stock price appreciation, reaffirming the central role of financial health in determining market valuation.
Please read the top 15 articles explaining share price:
How to find the price per share?
What Happens to Share Price After Buyback?
What makes a share price go up?
What causes share prices to drop?
How do you calculate the share average price?
How do you calculate the share price from the Balance Sheet?
Why do stock buybacks increase share price?
Do stock splits increase share price?
Does dividend reduce share price?
How does debt affect share price?
How does issuing new shares affect share price?
How to calculate the share price of a startup company?
What happens if a share price goes to zero?
























